
RFID know-how has remodeled the way in which companies and organizations monitor and handle property, stock, and data. It operates by using electromagnetic fields to mechanically establish and seize information from tags hooked up to things, with out requiring a direct line of sight, enabling sooner and extra environment friendly information assortment in comparison with barcodes. As industries more and more search progressive options to reinforce operational effectivity and enhance buyer expertise, RFID has develop into a vital device for a variety of purposes, from provide chain administration to entry management. This text will information you thru this exceptional know-how.
What’s RFID Know-how
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) know-how is a wi-fi communication methodology that makes use of electromagnetic fields to mechanically establish and monitor tags hooked up to things. It permits for information seize with out the necessity for a direct line of sight, making it a extremely environment friendly answer for quite a lot of purposes.

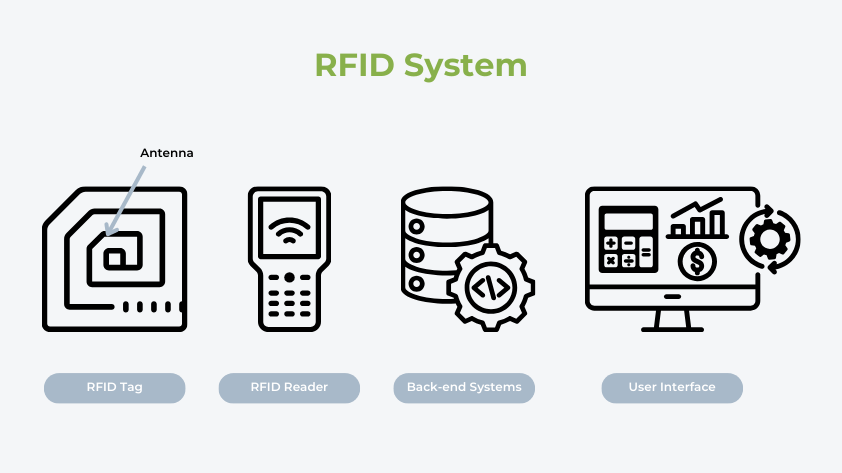
Parts of RFID Programs
RFID programs include a number of key elements that work collectively to allow automated identification and information seize. Listed below are the primary elements:
RFID Reader
The RFID reader is a central gadget that transmits radio waves to activate RFID tags. It receives the sign despatched again by the tag and decodes the data.
Readers will be handheld or fastened (mounted in a particular location) and are available numerous sorts to go well with completely different purposes and environments.
RFID Tag
RFID tags are small units that include a microchip and an antenna. They retailer a novel identifier and, in some circumstances, extra information concerning the object they’re hooked up to.
Tags will be divided into three classes:
Passive tags: don’t have any inside energy supply; they depend on the reader’s power to transmit information.
Energetic tags: have an inside battery, permitting them to ship indicators over longer distances.
Semi-passive tags: use a battery for inside features however nonetheless depend on the reader for communication.
Antenna
The antenna facilitates communication between the RFID reader and the tag. It transmits radio waves to activate the tag and receives the sign despatched again by the tag.
Antennas are available quite a lot of sizes and shapes, designed to optimize the vary and efficiency of the RFID system.
Again-end Programs
The back-end system consists of software program and databases that course of information acquired from RFID readers. It handles information storage, evaluation, and reporting.
The system will be built-in with different enterprise programs, reminiscent of stock administration or ERP programs, to enhance operational effectivity.
Consumer Interface
The consumer interface supplies entry to processed information, permitting customers to observe, analyze, and handle RFID-related info. This may occasionally embrace dashboards, reporting instruments, or alert programs to inform customers of essential adjustments.
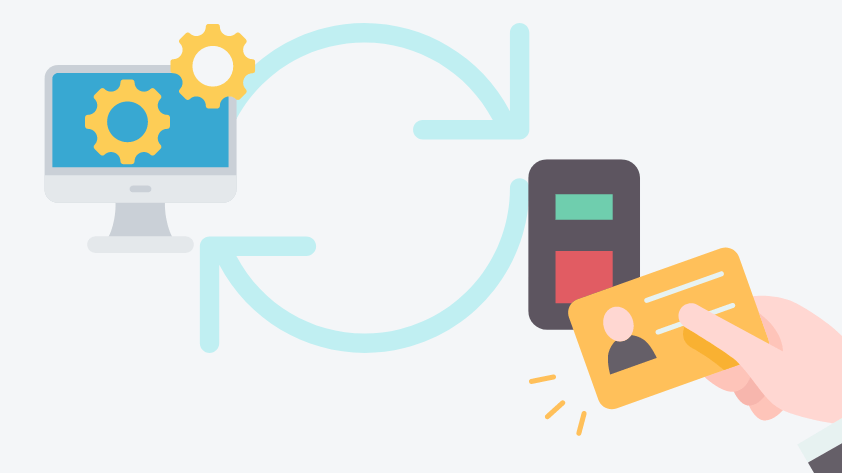
How RFID Works
RFID know-how operates by way of a easy but efficient communication course of between an RFID reader and an RFID tag. Right here’s an in depth breakdown of the way it works:
RFID Reader Transmits Radio Waves
RFID readers transmit radio waves, creating an electromagnetic area. This area is used to activate close by RFID tags.
Tag Activation
When an RFID tag enters the reader’s area, it receives power from the reader’s radio waves (within the case of passive tags) or attracts by itself energy supply (within the case of energetic tags). This activation causes the tag to transmit its distinctive identifier and any saved information again to the reader.
Information Transmission
The activated tag sends its info through radio waves. This communication doesn’t require line of sight, which differentiates RFID from conventional barcode programs.
Information Seize by Reader
The RFID reader receives the sign from the tag. It decodes the data and processes it for additional use. Relying on the system, a number of tags will be learn concurrently, growing effectivity.
Integration with Backend Programs
The reader sends the decoded information to the backend system for processing. The system analyzes the data, updates the database, and generates studies. It could possibly additionally combine with present enterprise programs, reminiscent of stock administration software program, to streamline operations.
Consumer Entry
Customers can entry processed information by way of a consumer interface, which can embrace dashboards, alerts, and reporting instruments. This enables for real-time monitoring and decision-making primarily based on the captured information.
Video Tutorial
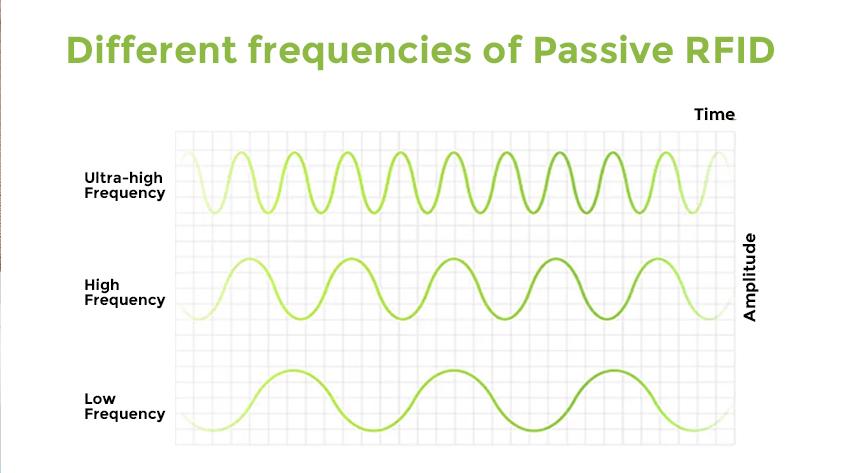
Completely different frequencies of Passive RFID
Passive RFID tags function in several frequency ranges, every with completely different traits, advantages, and typical purposes. The three essential frequency bands for passive RFID are low frequency (LF), excessive frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF). Every band is described intimately under:
Low Frequency (LF)
Frequency Vary: 125 kHz to 134 kHz
Learn Vary: Usually as much as 10 cm (4 in)
Options: LF RFID is much less delicate to interference from metallic and liquids, making it appropriate for purposes the place such supplies are current. Nonetheless, LF tags have a slower information switch charge and shorter learn vary than increased frequencies.
Frequent Functions: Animal monitoring, entry management (e.g., key fobs), and a few industrial purposes.
Excessive Frequency (HF)
Frequency Vary: 13.56 MHz
Learn Vary: Usually as much as 1 m (3 ft)
Options: HF RFID is extensively used due to its stability between learn vary and information switch velocity. It’s higher suited to environments with restricted interference and is usually utilized in purposes that require shut proximity.
Frequent Functions: Library e book monitoring, sensible playing cards (e.g., contactless fee programs), and ticketing programs.
Extremely Excessive Frequency (UHF)
Frequency Vary: 860 MHz to 960 MHz
Learn Vary: As much as 12 meters (39 ft) or extra, relying on the tag and reader
Options: UHF RFID gives the longest learn vary and quickest information switch charges, making it splendid for monitoring gadgets over lengthy distances. Nonetheless, UHF indicators will be affected by interference from water and metallic.
Frequent Functions: Provide chain administration, stock monitoring, asset administration, and logistics.
Key Markets and Software Areas
RFID know-how is flexible and has been utilized in quite a few industries. Right here’s an in depth have a look at the key markets and utility areas:
Retail
Stock Administration: RFID allows retailers to conduct real-time stock audits. By tagging gadgets, retailers can instantly decide inventory ranges, decreasing discrepancies resulting from theft or misplacement. The know-how additionally permits for automated reordering processes when stock falls under predefined ranges.
Asset Monitoring: Retailers can use RFID tags to observe high-value gadgets, reminiscent of electronics or luxurious items. This reduces the time workers spend looking for merchandise and improves stock replenishment effectivity.
Buyer Expertise: RFID improves customer support by enabling a sooner checkout course of. For instance, RFID-enabled self-checkout kiosks enable clients to scan a number of gadgets directly, decreasing wait occasions and growing total buying satisfaction.
Logistics and Provide Chain
Asset Monitoring: RFID tags hooked up to pallets or containers present visibility all through the provision chain. This enables corporations to trace shipments in actual time, decreasing delays and guaranteeing well timed supply.
Transport and Receiving: At loading docks, RFID programs can mechanically verify incoming and outgoing items, guaranteeing correct counts and decreasing human error. This will scale back processing time and enhance warehouse operational effectivity.
Warehouse Administration: RFID know-how simplifies stock administration in warehouses. It permits for automated stock counts and real-time visibility into stock ranges, minimizing the chance of out-of-stock or overstocking.
Healthcare
Affected person Monitoring: RFID wristbands are used to establish sufferers, guaranteeing correct treatment administration and decreasing the chance of medical errors. Hospitals can rapidly find sufferers inside the facility, bettering total affected person security.
Asset Administration: RFID tags will be hooked up to costly medical tools, permitting hospitals to trace utilization and forestall loss. This ensures vital tools is available when wanted.
Treatment Administration: RFID know-how might help confirm drugs on the level of care. By scanning RFID tags on affected person wristbands and drugs, healthcare suppliers can guarantee they’re utilizing the right treatment and dosage.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing Line Monitoring: RFID tags can monitor elements and supplies in the course of the manufacturing course of. This visibility helps producers optimize workflows, scale back bottlenecks, and enhance total manufacturing effectivity.
High quality Management: By tagging merchandise at numerous levels, producers can be certain that high quality requirements are met. RFID programs can report information about inspections and high quality checks, streamlining audits and regulatory compliance.
Transportation and Logistics
Fleet Administration: RFID tags affixed to automobiles allow fleet managers to observe car location, gas consumption, and upkeep schedules. This information will be analyzed to enhance route planning and scale back working prices.
Toll Assortment: RFID know-how is extensively utilized in digital toll assortment programs. Automobiles outfitted with RFID tags can go by way of toll cubicles with out stopping, decreasing congestion and shortening journey occasions for drivers.
Entry Management and Safety
Constructing Entry: RFID key playing cards or badges can management entry to safe areas, permitting solely approved personnel to enter. This enhances safety and supplies a report of who has visited sure areas at a particular time.
Asset Safety: RFID programs can set off an alarm if a tagged merchandise is faraway from a chosen space with out correct authorization. That is significantly helpful in high-value environments reminiscent of museums or retail shops.
Agriculture
Livestock Monitoring: RFID tags affixed to livestock assist farmers monitor well being standing, breeding historical past, and motion patterns. This information helps handle herds extra successfully and guarantee compliance with well being laws.
Provide Chain Traceability: By tagging agricultural merchandise, farmers can monitor their items as they journey from farm to market. This traceability improves meals security and permits shoppers to confirm the origin of their meals.
Occasion Administration
Ticketing: RFID wristbands or playing cards streamline the admission course of for occasions, concert events, and festivals. They permit for fast scanning and also can embrace cashless fee capabilities, bettering attendee comfort.
Attendee Monitoring: Organizers can use RFID know-how to observe attendee exercise and engagement throughout an occasion. This information helps optimize future occasion planning and enhance attendee expertise.

Predominant Advantages of RFID
RFID know-how gives quite a few advantages to numerous industries, bettering effectivity, accuracy, and total operational efficiency. Listed below are among the key advantages:
Improved Stock Administration
RFID can monitor stock ranges in actual time, serving to companies preserve optimum stock ranges and scale back out-of-stock or overstock conditions.
Automated stock audits scale back handbook counts and enhance accuracy, permitting for higher stock management.
Enhanced Information Accuracy
RFID minimizes human errors related to handbook information entry. Automated information seize ensures extra correct monitoring of things and administration of property.
With RFID programs, companies can scale back discrepancies in stock information, permitting for higher decision-making.
Elevated Effectivity
RFID permits a number of gadgets to be scanned concurrently, vastly rushing up processes reminiscent of retail checkout and warehouse stock audits.
By streamlining operations, RFID reduces labor prices and time spent on handbook monitoring.
Actual-Time Visibility
RFID supplies real-time information on the placement and standing of things all through the provision chain. This visibility helps companies reply rapidly to adjustments and enhance total provide chain administration.
Firms can monitor property in transit, bettering their skill to successfully handle logistics and deliveries.
Enhanced Safety and Loss Prevention
RFID tags can enhance asset safety by triggering an alarm if an unauthorized merchandise is faraway from a safe space.
In retail, RFID know-how helps higher monitor high-value gadgets, decreasing theft and shrinkage.
Value Financial savings
Whereas preliminary implementation prices will be excessive, long-term financial savings from lowered labor, improved stock accuracy, and loss prevention usually outweigh these prices.
Elevated effectivity can scale back working prices and enhance profitability.
Higher Buyer Expertise
In retail, RFID can improve the client buying expertise by rushing up checkout and bettering product availability.
Correct stock monitoring ensures standard gadgets are in inventory, decreasing buyer frustration.
Traceability and Compliance
RFID know-how can higher monitor merchandise all through the provision chain, which is vital for industries reminiscent of meals and prescribed drugs that want to stick to strict security laws.
This traceability can simplify audits and enhance operational transparency.
Integration with Different Applied sciences
RFID can simply combine with different applied sciences, such because the Web of Issues (IoT) and information analytics programs, permitting corporations to realize deeper insights into their operations and make data-driven selections.
This integration can improve predictive upkeep, optimize workflows, and enhance total enterprise intelligence.

Completely different RFID Product Sorts
RFID tags are available quite a lot of bodily kinds, every tailor-made for particular purposes and environments. Listed below are the primary sorts of RFID tags primarily based on their type:
Inlays
Composed of a chip and antenna embedded in a substrate. Inlays will be transformed into numerous tag codecs (e.g., stickers,labels).
Generally utilized in retail for merchandise tagging, packaging, and logistics.
Labels
Labels are RFID inlays encapsulated in a substrate reminiscent of paper or plastic, with an adhesive backing for simple utility.
Splendid for stock administration, delivery labels, and retail worth tags.
Playing cards
RFID tags are within the type of standard-sized playing cards, just like bank cards.
Utilized in entry management, worker identification, and fee programs.
Key Fobs
Small, transportable RFID tags designed to suit on a key fob, often housed in a rugged plastic housing.
Generally utilized in entry management programs.
Wristbands
Versatile RFID tags built-in into wristbands product of silicone or material.
Extensively utilized in occasions, theme parks, and hospitals to trace attendance and handle entry.
Button Tags
Small, spherical RFID tags that resemble buttons and are sometimes encapsulated in sturdy supplies.
Splendid for asset monitoring in industrial settings.
Embedded Tags
RFID tags which might be embedded in merchandise or supplies in the course of the manufacturing course of (e.g., textiles, plastics).
Utilized in attire and shopper items for seamless monitoring.
Sensor Tags
RFID tags with built-in sensors to observe environmental circumstances (e.g., temperature, humidity).
Generally utilized in chilly chain industries, prescribed drugs, and meals logistics to make sure merchandise stay in specified circumstances.
LED Tags
RFID tags outfitted with LED lights that present visible suggestions or alerts primarily based on the standing or situation of the tag.
Splendid for stock administration and retail to point that an merchandise is low in inventory or has been efficiently scanned.
Cable Tie Tags
RFID tags within the type of cable ties, usually used to safe gadgets or as non permanent tags.
Splendid for out of doors actions, stock management, and tagging gadgets that have to be simply put in and eliminated.
Twin-Frequency Tags
These tags are in a position to function in two completely different frequency bands (e.g., LF and HF or HF and UHF) for elevated versatility.
They’re appropriate for purposes that require compatibility with completely different RFID programs, reminiscent of provide chain logistics, the place each short-range and long-range studying are required.

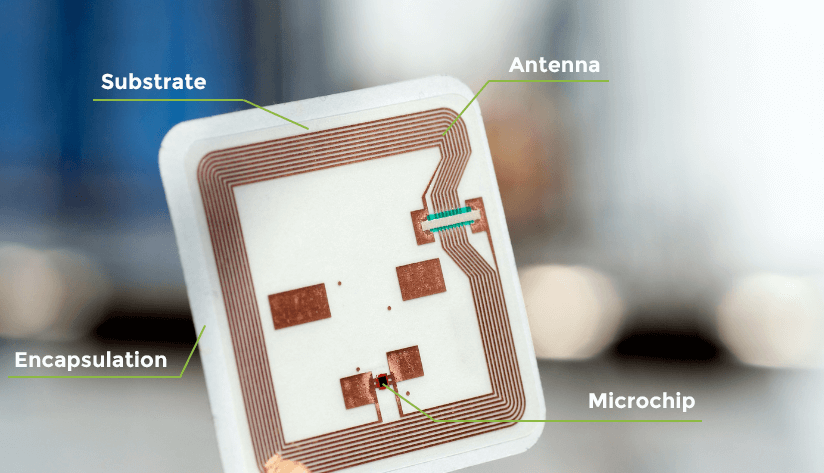
How an RFID Tag is Constructed
RFID tags are made up of a mix of elements that work collectively to allow wi-fi communication. Here’s a breakdown of RFID tag building:
Microchip
The microchip is the guts of the RFID tag and accommodates the distinctive identifier and every other information. It processes the indicators acquired from the RFID reader and controls the tag’s performance.
Antenna
The antenna is important for communication. It converts electromagnetic waves from the RFID reader into electrical indicators that energy the chip. The design and measurement of the antenna differ relying on the frequency and utility.
Substrate
The substrate serves as a base layer that gives assist for the chip and antenna. It’s often product of supplies reminiscent of plastic or paper, that are chosen for his or her sturdiness and adaptability.
Encapsulation
This protecting layer protects the chip and antenna from environmental components reminiscent of moisture, mud, and bodily harm. Encapsulation supplies can embrace resins, silicones, or sturdy plastics.
Adhesive Layer (Non-obligatory)
Some RFID tags have an adhesive layer on one aspect that permits for simple attachment to quite a lot of surfaces. This layer ensures that the tag stays securely fastened throughout use.
Extra Options
Some tags might embrace built-in sensors for monitoring circumstances reminiscent of temperature or humidity, or LED indicators that present visible suggestions on the tag’s standing.
RFID Tag vs. RFID Inlay
RFID tags and RFID inlays play completely different roles in RFID know-how, with inlays additional divided into dry and moist inlays. Here’s a detailed comparability of those features:
RFID Tags
An RFID tag is an entire unit consisting of an RFID chip, an antenna, substrate, and often extra elements reminiscent of a protecting case or adhesive backing.
RFID Inlays
RFID inlays are the core part, divided into dry and moist inlays, together with the RFID chip, antenna, and substrate, with moist inlays additionally having an adhesive layer, however missing in depth protecting layers or options. It serves as the premise for an RFID tag.
Dry Inlays: These inlays don’t have any adhesive backing and are designed to be built-in into different supplies, reminiscent of tags or playing cards. Lighter and extra versatile, they’re appropriate for quite a lot of purposes and require extra supplies to connect.
Moist Inlays: Moist inlays include an adhesive layer that permits them to be simply hooked up to a floor. This built-in adhesive will be utilized on to the product or packaging.
Typically extra sturdy than dry inlays, they’re designed for purposes that require fast attachment, reminiscent of retail or logistics.
Key Variations Between RFID Tags and Inlays
Integrity: RFID tags are absolutely practical and able to deploy, whereas RFID inlays are elements that require extra supplies to be put into use.
Sturdiness: Tags often have a protecting casing, whereas inlays might lack essential packaging, so the sturdiness of tags is usually stronger than that of inlays.
Use Surroundings: Tags are appropriate for direct utility in quite a lot of environments, whereas inlays are primarily utilized in manufacturing and integration processes.
RFID vs. NFC
RFID and NFC (Close to Subject Communication) are each wi-fi communication applied sciences, however they serve completely different functions and function in distinct methods.. Here’s a comparability of the 2:
Definition
RFID: A know-how that makes use of radio waves to mechanically establish and monitor tags hooked up to things. It really works at completely different distances relying on the kind of RFID system (LF, HF, UHF).
NFC: As a subset of RFID know-how, NFC operates at a particular frequency (13.56 MHz) and is designed for short-range communication, usually inside a number of centimeters.
Frequency and Vary
RFID: Operates throughout a number of frequency bands (low frequency, excessive frequency, ultra-high frequency). The learn vary can vary from a number of centimeters (LF) to tens of meters (UHF), relying on the system and tag kind.
NFC: Operates solely at 13.56 MHz. The learn vary is often restricted to a couple centimeters (often about 4 cm or much less), guaranteeing close-range communication.
Communication Modes
RFID: Helps each one-way (reader to tag) and two-way (reader and tag) communication. Tags will be passive, energetic, or semi-passive, which impacts how information is transferred.
NFC: Primarily used for two-way communication. Each units (reader and tag) can provoke an trade. NFC is simple to make use of and often requires a consumer motion (e.g., tapping a smartphone) to provoke communication.
Functions
RFID: Generally used for stock administration, asset monitoring, provide chain administration, and entry management. Extensively utilized in retail, logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing.
NFC: Primarily used for contactless funds, cell ticketing, and safe information trade. Generally utilized in retail, public transportation, and cell purposes.
Safety
RFID: Varies vastly relying on implementation; passive RFID will be much less safe du to its vary and long-distance studying capabilities.
NFC: Typically safer resulting from its quick vary and requires close-range communication. Typically mixed with encryption and authentication protocols to make sure safe transactions.

RFID vs. Barcode
RFID and barcodes are each applied sciences used to trace and establish gadgets, however they’ve completely different traits, benefits, and limitations. Here’s a comparability of the 2:
Definition
RFID: A know-how that makes use of radio waves to mechanically establish and monitor tags hooked up to things. RFID programs include readers, tags, and backend programs.
Barcode: A visible illustration of information in a particular format, often consisting of parallel strains (1D) or a grid sample (2D). Barcodes are scanned utilizing optical scanners.
Information Storage
RFID: Can retailer quite a lot of information sorts, together with distinctive identifiers, product info, and even sensor information. As well as, many RFID tags enable information to be up to date or rewritten.
Barcode: Normally restricted to a numeric or alphanumeric code similar to a product. A normal barcode can often retailer about 20-25 characters. As soon as printed, the information encoded within the barcode can’t be modified.
Scanning Strategies
RFID: Makes use of radio waves to speak, RFID tags will be learn at a distance with out line of sight, RFID readers can learn a number of tags on the identical time, making scanning massive quantities of stock extra environment friendly.
Barcode: Requires line of sight for scanning. The barcode should be seen to the scanner. Normally one merchandise is learn at a time, which may decelerate processing in high-volume environments.
Vary
RFID: Relying on the system used, the vary can differ from a number of centimeters (for passive tags) to over 100 meters (for energetic tags).
Barcode: Restricted to a couple inches as a result of the scanner should be near the barcode.
Value
RFID: Typically dearer resulting from the price of the tag and reader. Nonetheless, prices have been lowering because the know-how advances. Due to this fact, it could possibly considerably enhance operational effectivity and scale back labor prices in the long term.
Barcode: Each the barcode and the scanner are typically low, so it’s a cost-effective answer for a lot of companies. But it surely has prices when it comes to printing new labels for product adjustments or updates.
Functions
RFID: Generally used for stock administration, asset monitoring, provide chain logistics, and entry management. Frequent in industries reminiscent of retail, healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation.
Barcode: Extensively utilized in retail product labeling, stock management, and transportation logistics. Frequent in retail, warehousing, and manufacturing.
Safety
RFID: Varies vastly relying on implementation; passive RFID will be much less safe resulting from its vary and long-distance studying capabilities.
Barcode: Typically much less safe as a result of barcodes will be simply copied or tampered with.

RFID Requirements
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) requirements are a vital basis for guaranteeing that RFID programs can interoperate and performance effectively throughout completely different units, purposes, and industries. These requirements cowl numerous features of RFID, together with communication protocols, information codecs, frequency band utilization, efficiency necessities, and safety. Right here’s an in depth introduction to RFID requirements:
ISO Customary Sequence
ISO (Worldwide Group for Standardization) is likely one of the essential builders within the area of RFID standardization. It supplies a sequence of requirements to control numerous features of RFID programs and guarantee world compatibility.
ISO 18000 Sequence
The ISO 18000 sequence of requirements defines the air interface protocol for RFID programs working in several frequency ranges (i.e., how readers and tags talk).
ISO 18000-1: Basic specs, fundamental technical necessities, and air interface definitions relevant to all RFID frequency bands.
ISO 18000-2: Low frequency (LF) customary, masking a frequency vary of 125 kHz to 134 kHz, generally used for animal identification and industrial purposes. This customary defines the bodily layer and communication protocol for low-frequency RFID programs.
ISO 18000-3: Excessive frequency (HF) customary, masking the 13.56 MHz frequency vary, used for NFC, sensible playing cards, and merchandise monitoring. This frequency band is extensively utilized in entry management programs, fee, and ticketing purposes.
ISO 18000-4: Standardizes low-power purposes of ultra-high frequency (UHF) programs, usually working within the 2.45 GHz frequency band.
ISO 18000-6: Extremely-high frequency (UHF) customary, masking the 860 MHz to 960 MHz frequency vary, generally utilized in provide chain administration and logistics. This customary is especially essential as a result of it helps the EPCglobal Gen 2 protocol, which is extensively used within the retail and logistics industries.
ISO 18000-7: Energetic RFID customary relevant to 433 MHz energetic RFID tags, which have their very own energy provide and will be learn and written over lengthy distances, generally utilized in asset administration and logistics monitoring.
Different ISO Requirements
ISO 11784/11785: Low frequency (LF) RFID customary for animal identification, defining the information construction and communication protocol of the tag, extensively utilized in livestock administration.
ISO 15693: RFID system particularly for 13.56 MHz excessive frequency (HF) lengthy learn vary, widespread in areas reminiscent of library administration and manufacturing unit automation.
ISO/IEC 14443: This customary is used for Close to Subject Communication (NFC) units, supporting contactless sensible playing cards and fee purposes like financial institution playing cards and transit playing cards.
EPCglobal Requirements
EPCglobal is a corporation devoted to creating requirements for RFID purposes in provide chain administration. It’s a part of GS1 and is accountable for the event of world provide chain requirements.
EPC Gen 2
EPCglobal Class 1 Technology 2 (EPC Gen 2) is likely one of the most generally used RFID requirements, masking the UHF band (860-960 MHz) for interoperability of tags and readers within the world provide chain. This customary primarily specifies the communication protocol, information construction, and bodily layer specs of the tag to make sure that tags and readers from completely different producers can work seamlessly.
Options:
1. It consists of anti-collision know-how and might learn a number of tags directly.
2. It has information encryption to reinforce safety.
3. It’s extensively used for monitoring merchandise and managing stock within the retail trade.
EPC Encoding Customary
EPCglobal has additionally developed the EPC encoding customary, which specifies the right way to retailer and transmit Digital Product Codes (EPC) in RFID tags, permitting merchandise to be tracked uniformly worldwide. EPC is a globally distinctive identifier extensively used to trace and handle items within the provide chain.
GS1 Requirements
GS1 is the primary developer of world provide chain administration requirements, and RFID requirements are a key a part of its choices. The GS1 RFID customary is intently associated to the EPCglobal customary, particularly within the logistics, retail, and fast-moving shopper items industries.
GS1 EPC/RFID customary: Offers detailed tips on the right way to use EPC and RFID know-how to trace and handle the provision chain, masking your complete course of from label encoding to information processing and sharing.
International Information Synchronization Community (GDSN): This customary specifies the right way to synchronize and share product information globally by way of RFID tags and EPC codes to make sure transparency and effectivity within the provide chain.
AIM Requirements
AIM (Automated Identification and Mobility) is a worldwide group accountable for automated identification know-how requirements, together with barcode and RFID requirements. It has revealed a sequence of RFID requirements, significantly for tags utilized in specialised environments.
The AIM DPM (Direct Half Marking) Customary specifies the right way to mark RFID tags straight on the floor of merchandise or elements to be used in places the place conventional RFID tags can’t be used, reminiscent of metallic or high-temperature environments. Such requirements are sometimes utilized in industries like aviation, automotive, and protection.
Safety Requirements in RFID Programs
With the widespread utility of RFID know-how, information safety has develop into more and more essential. ISO and different requirements organizations have developed numerous safety requirements to guard the integrity of RFID communications and information.
ISO/IEC 29167: Covers encryption and safety protocols in RFID programs, defining the right way to securely transmit information between RFID tags and readers to stop eavesdropping and counterfeiting.
NIST SP 800-162: Revealed by the Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Know-how (NIST), it supplies steering on RFID system safety, masking authentication, encryption, and entry management.
RFID Customary Functions in Completely different Industries
Completely different industries have various necessities for RFID, resulting in particular requirements for specific sectors. For instance:
Retail: Companies extensively use the EPC Gen 2 customary for stock administration and theft prevention.
Healthcare: The ISO 18000-3 high-frequency customary tracks and manages tools and drugs.
Aviation and Automotive: The AIM DPM customary allows producers to straight mark RFID tags on metallic elements.
Logistics and Transportation: The UHF RFID (ISO 18000-6) customary allows the long-distance monitoring of containers and items.

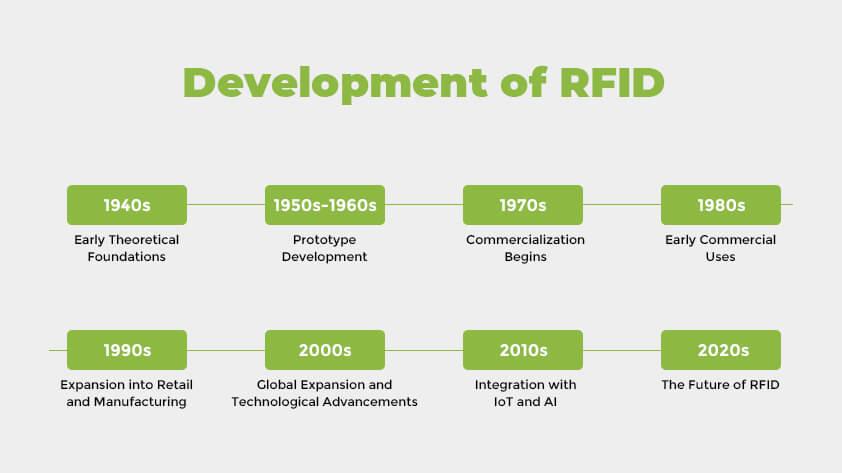
Development of RFID
RFID know-how has a protracted historical past, courting again to the mid-Twentieth century, with important technological developments occurring in levels.
Nineteen Forties: Early Theoretical Foundations
Origins of Radar Know-how: Radar and identification programs used throughout World Battle II laid the conceptual basis for RFID. The British Military utilized a rudimentary type of RFID in its Identification Good friend or Foe (IFF) system, which employed radio waves to differentiate between pleasant and enemy plane.
Harry Stockman’s Analysis (1948) : Stockman revealed a seminal paper titled “Communication by Mirrored Energy” that laid the theoretical basis for RFID know-how.
Nineteen Fifties-Sixties: Prototype Growth
Scientific Exploration: Throughout this era, RFID remained a curiosity within the scientific neighborhood, specializing in analysis into the right way to use radio waves to speak info wirelessly.
The First RFID-Like Programs: Researchers performed experiments to create early RFID-like programs for monitoring, stock management, and safety. The principle limitations on the time have been the dearth of compact know-how and energy sources.
Seventies: Commercialization Begins
First RFID Patent: Within the Seventies, inventors issued the primary RFID-related patent, marking the start of commercialization. Firms started experimenting with RFID for livestock monitoring, car toll programs, and anti-theft options.
Los Alamos Nationwide Laboratory: Scientists at Los Alamos Nationwide Laboratory in New Mexico developed passive RFID know-how for nuclear materials monitoring, representing a significant leap ahead within the sensible utility of RFID.
Nineteen Eighties: Early Business Makes use of
Entry Management and Safety Programs: Firms started making use of RFID in sensible makes use of reminiscent of entry management for workplace buildings and automobile key safety programs.
Transportation and Tolling: Transportation programs launched RFID know-how for freeway tolling, utilizing RFID tags to establish automobiles and eradicate the necessity for handbook fee.
Provide Chain Monitoring: Firms like IBM began exploring RFID for provide chain administration to trace stock and handle manufacturing strains.
Nineties: Enlargement into Retail and Manufacturing
Standardization Efforts: The Nineties noticed elevated efforts to standardize RFID know-how, making it simpler to undertake throughout industries. The Digital Product Code (EPC), developed by the MIT Auto-ID Heart, was a major step in standardizing RFID for retail and provide chain purposes.
Adoption by Massive Firms: Main companies reminiscent of Walmart started using RFID to reinforce their provide chain logistics, driving the know-how ahead.
Livestock RFID Tags: Firms launched RFID programs to trace livestock, significantly for regulatory and well being monitoring functions.
2000s: International Enlargement and Technological Developments
Extremely-Excessive Frequency (UHF) RFID: UHF RFID grew to become extra prevalent resulting from its longer learn vary and skill to trace gadgets at larger distances and speeds. UHF was essential for RFID’s growth into retail, logistics, and industrial purposes.
Decrease Prices and Wider Adoption: Advances in semiconductor know-how considerably lowered the price of RFID tags and readers. Coupled with will increase in computing energy, RFID grew to become extra accessible to companies of all sizes.
Retail Necessities: Walmart and the U.S. Division of Protection started requiring their suppliers to make use of RFID tags on items, accelerating adoption in manufacturing and logistics.
2010s: Integration with IoT and AI
Integration with the Web of Issues (IoT) : Within the 2010s, corporations built-in RFID into the bigger IoT ecosystem, enabling real-time monitoring and monitoring of merchandise, property, and folks.
AI and Information Analytics: RFID programs more and more leveraged AI and information analytics to extract insights from the huge quantities of information collected. This allowed industries to carry out predictive upkeep, automate decision-making, and optimize provide chains.
RFID in Healthcare: The healthcare trade started utilizing RFID for affected person monitoring, tools administration, and medicine monitoring to make sure higher security and effectivity.
2020s and Past: The Way forward for RFID
Sustainability and the Round Economic system: As curiosity in sustainability grows, corporations are utilizing RFID to observe the lifecycle of merchandise, from manufacturing to disposal, and to assist round economic system initiatives by bettering recycling and useful resource administration.
Superior RFID Tags: RFID tags have gotten extra refined, incorporating extra sensors to observe environmental circumstances reminiscent of temperature and humidity, making them appropriate for a wider vary of purposes, together with chilly chain administration for meals and prescribed drugs.
Smarter Cities and the Web of Issues: RFID continues to play a key position in sensible metropolis purposes, together with visitors administration, parking programs, and public transportation, offering seamless, real-time information to reinforce city dwelling.
Conclusion
RFID know-how effectively and flexibly identifies and tracks, making it extensively adopted throughout industries reminiscent of provide chain administration, sensible manufacturing, retail, and healthcare. It not solely enhances operational effectivity but in addition facilitates real-time information sharing and administration. As know-how continues to advance and combine with the Web of Issues, RFID will play an more and more important position, driving clever transformation throughout numerous sectors.
By means of steady value reductions, efficiency enhancements, and standardization efforts, RFID will additional develop its utility scope, creating extra worth for companies and society. On this quickly evolving digital age, RFID is undoubtedly one of many key driving forces behind future innovation and alter.
Rec-Merchandise

UHF RFID Printer

Built-in UHF RFID Reader

Multi-Protocol Desktop HF RFID Reader


RFID Antenna UHF
15-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
UHF Tag
4″x2″ 860-960MHz UHF RFID Label RFID M4D
UHF Tag
4″x4″UHF RFID Label Alien H3 | ISO18000-6C
RFID Antenna UHF
5-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 1K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 4K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight C
HF Tag
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight EV1
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag ATA5577
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4200
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4305
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID TAG 213