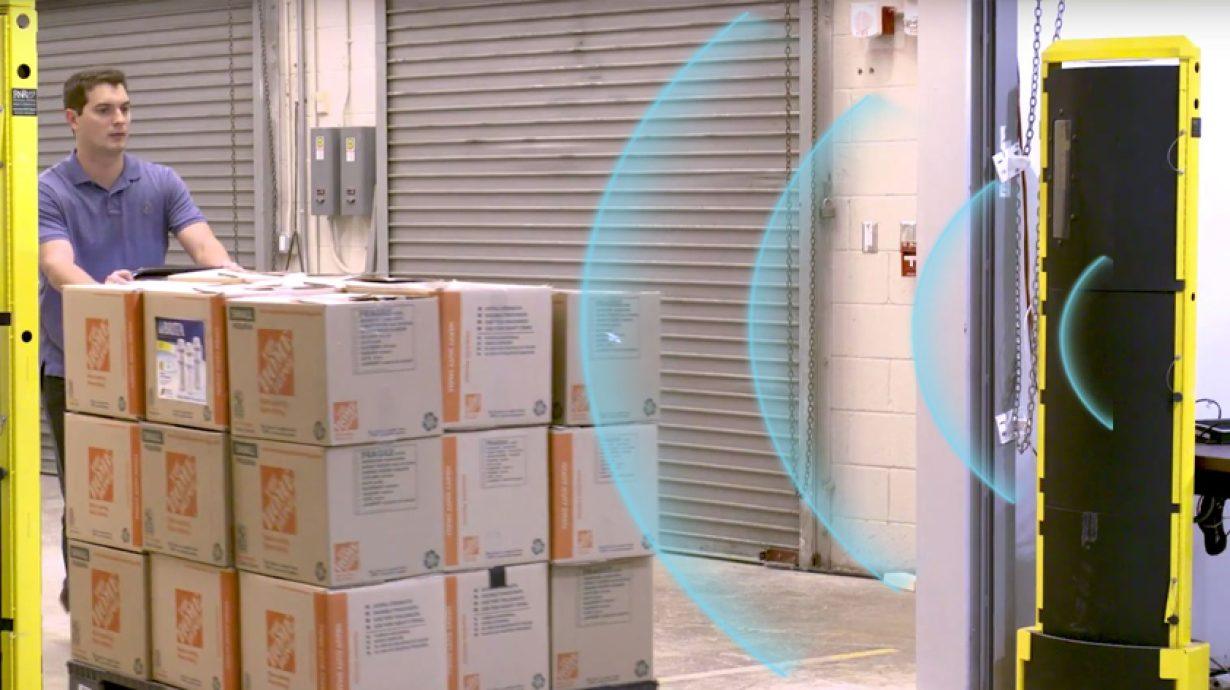

Think about you’re at a bustling airport looking for your gate among the many crowd and indicators. Now, consider an RFID antenna as your sensible information, serving to you pinpoint precisely the place you could go. Within the RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) world, antennas are essential instruments that make this magic occur. They’re important in sending and receiving indicators inside an RFID system, guaranteeing clean information movement between RFID tags and readers. Monitoring and managing property can be way more difficult with out these sensible gadgets. So, let’s dive into the world of RFID antennas and uncover how they work!
Understanding RFID Antennas
RFID antennas are essential parts in an RFID system, chargeable for transmitting and receiving radio frequency indicators between the RFID reader and tags. The antenna converts the electromagnetic waves emitted by the RFID reader into radio frequency indicators which might be despatched to the tags, and it additionally receives the data that the tags ship again. Its main position is to make sure correct information transmission, prolong the system’s studying vary, and improve the effectivity of real-time asset monitoring and administration. In fields like logistics and stock administration, RFID antennas make real-time information assortment doable, considerably boosting operational effectivity and accuracy.

Frequent Supplies for RFID Antennas
The efficiency of an RFID antenna closely relies on its materials. Frequent supplies used for RFID antennas embody:
Copper: Copper is likely one of the most generally used supplies for antennas as a consequence of its glorious conductivity. It successfully transmits electromagnetic waves, guaranteeing sturdy and steady indicators. Copper antennas are sometimes utilized in high-performance purposes, similar to industrial environments and high-frequency settings.
Aluminum: Aluminum is an economical various to copper and likewise affords good conductivity. Though it doesn’t match copper’s conductivity, it’s ample for a lot of purposes. Aluminum antennas are generally utilized in business and client RFID methods.
Graphite: Graphite is utilized for specialised purposes, significantly in high-temperature or corrosive environments. It affords glorious corrosion resistance, although it’s much less frequent.
The selection of fabric impacts the antenna’s efficiency, together with sign transmission effectivity, sturdiness, and price. Choosing the suitable materials can considerably improve the general efficiency of the RFID system.
How Do RFID Antennas Work?
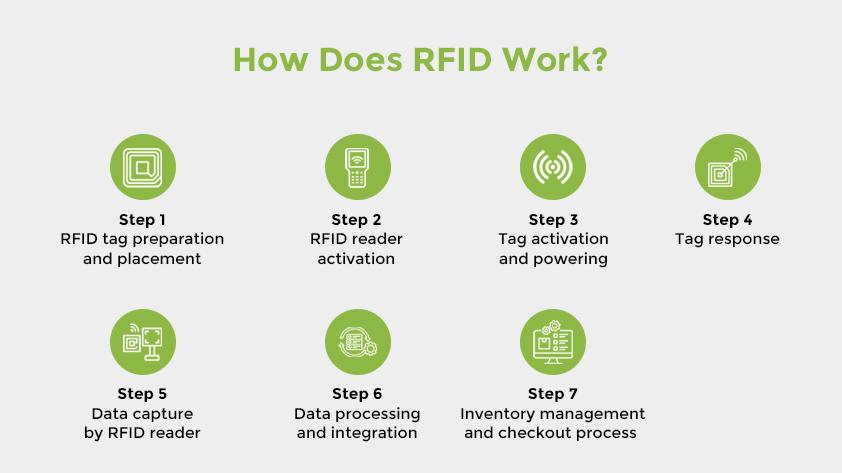
RFID antennas function based mostly on the transmission and reception of electromagnetic waves. Right here’s a step-by-step have a look at how they work:
Energy Reception: The antenna receives electrical vitality from the RFID reader. This vitality is then transformed into electromagnetic waves.
Sign Transmission: The electromagnetic waves are transmitted from the antenna, making a wi-fi communication hyperlink with close by RFID tags.
Tag Interplay: When an RFID tag enters the antenna’s sign protection space, it picks up the electromagnetic waves. The tag then responds with its personal sign.
Sign Reception and Information Trade: The antenna receives the tag’s response sign and sends it again to the RFID reader. This completes the information change course of.
Intimately, RFID antennas modulate the frequency and amplitude of electromagnetic waves to transmit information. These indicators journey by means of house at particular frequencies. When the antenna on the tag receives these indicators, it demodulates them to extract the data, which is then despatched again to the reader. The design of the antenna (together with its measurement, form, and materials) and its set up location have an effect on sign power and protection, which in flip determines the efficiency and effectivity of the RFID system.
What Is RFID Antenna Achieve and What Does It Do?
Achieve is a key parameter that describes the efficiency of an RFID antenna. It refers back to the antenna’s capability to transform enter electrical energy into radio frequency (RF) indicators, normally expressed in decibels (dB). Larger acquire means the antenna can convert energy right into a stronger sign extra successfully, enhancing each sign power and transmission distance.
In an RFID system, acquire instantly impacts efficiency:
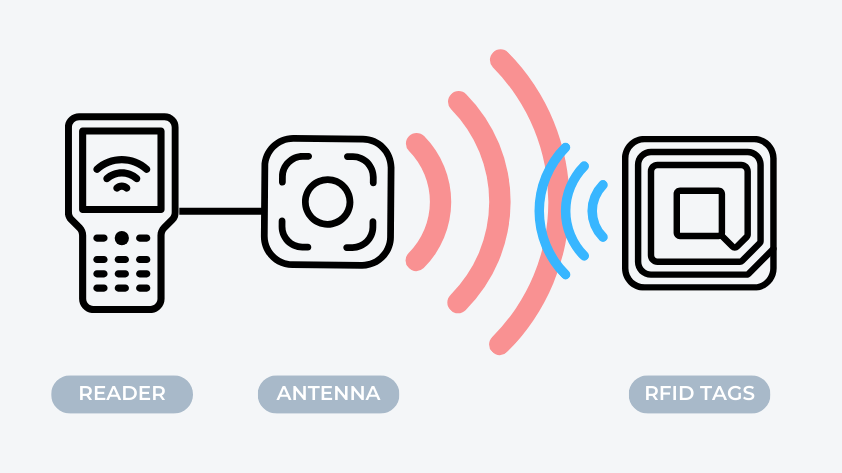
Studying Distance: Larger acquire antennas can transmit indicators over larger distances. This enables the RFID system to learn tags from farther away, increasing the system’s protection space.
Sign Protection: Antennas with excessive acquire present a broader sign protection space, lowering blind spots and weak sign zones. This ensures dependable tag studying in varied circumstances.
Sign Power: Excessive-gain antennas improve sign power, enhancing the steadiness and accuracy of information transmission. That is significantly essential in advanced environments with many obstacles or interference.
In abstract, the acquire of an RFID antenna determines the efficient studying vary and sign high quality of the system. It’s a necessary issue to think about when designing and choosing antennas.
Sorts and Classification of RFID Antennas
RFID antennas might be categorized based mostly on varied requirements. Listed below are the most typical sorts:
By Polarization:
Linear Polarized Antennas: These antennas emit electromagnetic waves that oscillate in a set aircraft. They’re appropriate for purposes the place the relative place of the tag and reader adjustments considerably. Linear polarized antennas are sometimes utilized in conditions requiring both horizontal or vertical polarization.
Round Polarized Antennas: These antennas produce electromagnetic waves that rotate in a round path. They’re much less delicate to the relative place of the tag and reader, making them superb for dynamic or advanced environments. Round polarized antennas can successfully obtain indicators even when tags are at varied angles.
By Construction:
Patch Antennas: Constructed from flat supplies, patch antennas are sometimes skinny and simple to put in. They’re well-suited for space-constrained environments, similar to cell gadgets or tags. Patch antennas supply good directivity and stability.
Dipole Antennas: Comprising two symmetrical conductors, dipole antennas usually present a bigger protection space and better acquire. They’re generally utilized in purposes requiring long-distance studying, similar to in warehouse and logistics administration.
Variations Between RFID Antennas and RFID Readers

RFID Antennas:
Perform: RFID antennas are chargeable for emitting and receiving indicators to speak with RFID tags. They play a vital position in enabling the wi-fi change of data between the tag and the reader.
RFID Readers:
Perform: RFID readers management the whole RFID system. They course of the indicators acquired from the antennas and transmit the information to pc methods for evaluation. The reader interprets the information from the tags and manages the general operation of the RFID system.
Selecting the Proper RFID Antenna:
When choosing an RFID antenna, contemplate the next components:
Utility Setting: Select the kind of antenna (e.g., patch or dipole) based mostly on set up house and environmental circumstances.
Achieve: Choose an antenna with the suitable acquire to match the required studying distance and sign protection.
Polarization: Select the right polarization (linear or round) to align with the orientation and mobility of the tags.
RFID Antenna Comparability Desk
| Sort | Polarization | Construction | Utility Situation | Benefits |
| Linear Polarized Antenna | Linear | Flat or 3D | Conditions with important relative motion between tag and reader | Delicate to place adjustments, sturdy directionality |
| Round Polarized Antenna | Round | Flat or 3D | Dynamic or advanced environments | Insensitive to tag angles, uniform protection |
| Patch Antenna | Linear or Round | Flat supplies | House-constrained purposes | Simple to put in, appropriate for small gadgets |
| Dipole Antenna | Linear | Symmetrical conductors | Lengthy-distance studying purposes | Large protection space, excessive acquire |
Choosing the suitable RFID antenna requires cautious consideration of those components to make sure optimum efficiency of the RFID system.
RFID Antenna Frequency Ranges
RFID antennas are available in three most important frequency ranges, every with its distinctive options and purposes:
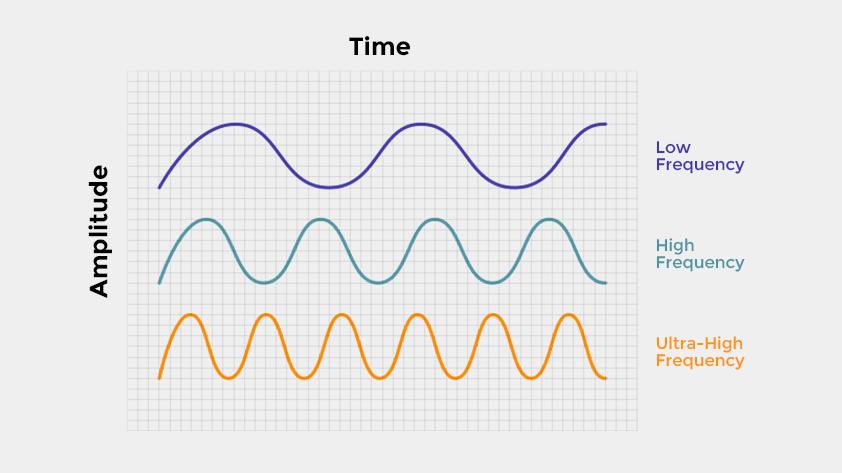
Low Frequency (LF, 125 kHz or 134.2 kHz)
- Traits: Brief learn vary (a number of centimeters to a number of centimeters), sturdy sign penetration, low interference.
- Functions: Ideally suited for animal identification and entry management the place short-range studying is required.
Excessive Frequency (HF, 13.56 MHz)
- Traits: Medium learn vary (a number of centimeters to 1 meter), quick information transmission, good interference resistance.
- Functions: Generally utilized in library administration, public transit playing cards, and cost methods.
Extremely Excessive Frequency (UHF, 860-960 MHz)
- Traits: Longest learn vary (a number of meters to over ten meters), sturdy sign penetration however extra delicate to interference.
- Functions: Extensively utilized in logistics, warehousing, and asset monitoring the place intensive protection is required.
Choosing the proper RFID antenna frequency vary based mostly in your utility ensures optimum system efficiency.
What’s the Learn Vary of UHF RFID Antennas?
UHF RFID antennas sometimes have a learn vary of a number of meters to over ten meters, making them appropriate for:
- Logistics and Warehouse Administration: Fast scanning and monitoring of products to reinforce stock administration effectivity.
- Provide Chain Administration: Actual-time monitoring of products in transit to optimize operations and enhance transparency.
- Asset Monitoring: Environment friendly administration of quite a few property, lowering loss threat and enhancing administration effectivity.
The long-range learn functionality and speedy processing of UHF RFID antennas make them glorious for purposes requiring intensive protection.
Frequent Functions of RFID Antennas

RFID antennas are broadly used throughout varied sectors to reinforce real-time information assortment and monitoring, resulting in elevated effectivity, decreased prices, and improved service high quality.
Cargo Monitoring in Provide Chain Administration: RFID antennas are used to trace the placement and standing of products in warehouses and through transportation. By putting in antennas at key factors, similar to warehouse entrances and transport automobiles, methods can robotically log the motion of products, enhancing logistics effectivity and lowering guide errors.
Hospital Gear Monitoring: Hospitals use RFID antennas to watch the placement of medical gear, guaranteeing well timed entry and utilization. For example, important surgical devices might be exactly situated in real-time utilizing RFID tags and antennas, stopping loss or misplacement of important gear.
Stock Administration in Retail Shops: RFID antennas might be put in on cabinets or at retailer entrances to robotically determine and file the motion of merchandise. This helps retailers optimize stock administration and forestall theft by offering real-time information on inventory ranges.
Entry Management at Massive Occasions: At occasions like concert events or exhibitions, RFID antennas are used to handle and file attendee entry. This ensures that solely people with legitimate tickets can enter particular areas, streamlining occasion operations and enhancing safety.
Find out how to Design and Set up RFID Antennas
Designing and putting in RFID antennas successfully is essential for optimizing system efficiency. Listed below are some sensible ideas for guaranteeing your RFID system operates at its greatest:
Antenna Peak: The set up top of the antenna can considerably impression sign protection. Ideally, the antenna ought to be mounted near the tags however not too low to keep away from bodily obstructions. Modify the peak based mostly on the applying (e.g., warehouses, retail shops) to maximise protection and reduce blind spots.
Antenna Angle: The angle at which the antenna is put in additionally impacts sign propagation. Sometimes, antennas ought to be aligned parallel or perpendicular to the tag’s floor to maximise sign reception and transmission effectivity. In dynamic environments, similar to automobiles or cell gadgets, make sure the antenna can regulate to accommodate totally different tag orientations and positions.
Sign Protection: To optimize sign protection, contemplate environmental components like obstacles and sources of interference. Modify the antenna’s acquire and directional design to reinforce sign power and prolong protection. Preserve enough distance from different gear or metallic objects to cut back sign attenuation.
Set up Location: Choosing the proper set up location is vital to sign stability and protection. In warehouses or factories, antennas might be put in at entry/exit factors, above cabinets, or in different strategic positions for environment friendly tag studying. Be sure that the set up doesn’t intrude with each day operations or gear motion.
Understanding these design and set up ideas will provide help to optimize your RFID system for correct and environment friendly information assortment. For extra in-depth steering on RFID antenna set up, try our earlier weblog submit: RFID Antenna Design and Set up Suggestions.
Find out how to Select the Proper RFID Antenna

Choosing the suitable RFID antenna is essential for optimizing your system’s efficiency. Listed below are key components to think about:
Utility Setting: Select an antenna that fits your particular atmosphere. For industrial settings, sturdiness and robustness are important, whereas in retail environments, aesthetics and measurement is likely to be extra necessary.
Studying Distance: The acquire of the antenna instantly impacts the studying distance. For purposes requiring long-range studying, a high-gain antenna is important, nevertheless it’s necessary to steadiness sign focus with protection vary.
Frequency Vary: The antenna’s frequency (similar to LF, HF, or UHF) ought to match the frequency of your RFID system. For instance, UHF antennas are appropriate for long-distance studying, whereas HF antennas are higher for close-range purposes.
Polarization: Select the polarization sort based mostly on the orientation of the tags and the antenna. Linear polarization is good for conditions the place the tag’s orientation is mounted, whereas round polarization is healthier for environments the place tag orientation might fluctuate.
Contemplating these components will assist you choose essentially the most acceptable RFID antenna to your wants, guaranteeing optimum efficiency and effectivity of your RFID system.
Challenges and Limitations of RFID Antennas
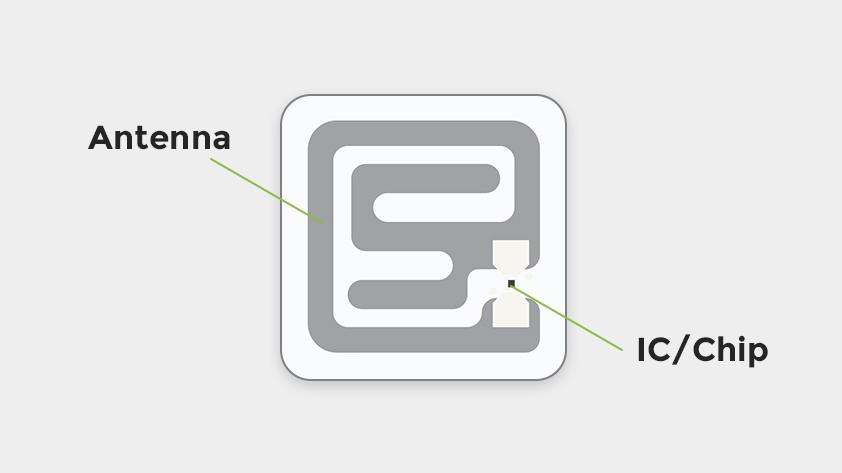
RFID antennas face a number of frequent challenges in sensible purposes, however with the suitable methods, these points might be successfully managed:
Sign Loss: In advanced environments, sign loss might be mitigated by choosing high-gain antennas and optimizing their set up areas. This ensures correct information studying even in difficult circumstances.
Interference Points: To keep away from frequency interference, detailed frequency planning and system administration are important. Correct coordination and configuration assist preserve the steadiness of the RFID system.
Price Considerations: Excessive-performance antennas might be costly. Nevertheless, by selecting cost-effective merchandise and aligning them with system wants, you may obtain optimum efficiency inside finances constraints.
Set up and Adjustment Difficulties: Putting in and adjusting antennas requires contemplating house and environmental limitations. Correct set up design {and professional} technical assist may help overcome these challenges successfully.
Addressing these challenges with considerate planning and skilled recommendation can improve the efficiency and reliability of your RFID system.
Conclusion
As expertise advances, RFID antennas have gotten extra environment friendly, steady, and adaptable. Improvements in supplies and reducing manufacturing prices are making RFID expertise extra accessible throughout varied industries at decrease prices. Moreover, the miniaturization and efficiency optimization of antennas will improve system reliability and protection.
To spice up effectivity, lower prices, and guarantee information accuracy, choosing the suitable RFID antenna is important. We provide a spread of high-performance antennas rigorously examined to carry out excellently in varied environments. When you’ve got any questions or want help discovering the right answer, be at liberty to achieve out to us. We’re right here that can assist you discover the best RFID antenna to your wants.
FAQs
1. What sort of antennas are used for RFID?
RFID methods sometimes use:
Linear Polarized Antennas: For mounted orientation tags.
Round Polarized Antennas: For dynamic or various tag angles.
Patch Antennas: Compact and flat, for tight areas.
Dipole Antennas: Large protection and excessive acquire, for big areas.
2. How does RFID work in easy phrases?
RFID makes use of radio waves to transmit information between a reader and a tag. The reader sends a sign, the tag responds with its info, and the reader processes this information.
3. Can RFID work with out an antenna?
No, RFID wants an antenna to ship and obtain indicators between the reader and the tag.
4. How are you going to optimize RFID antenna efficiency?
Place the antenna appropriately: Modify top and angle for greatest protection.
Select the suitable sort: Match acquire and polarization to your atmosphere.
Use high-gain antennas: For longer studying distances.
Preserve frequently: Verify for injury and alignment.
5. What’s the vary of RFID antennas?
Low Frequency (LF, 125 kHz): A couple of centimeters to some decimeters.
Excessive Frequency (HF, 13.56 MHz): As much as one meter.
Extremely Excessive Frequency (UHF, 860-960 MHz): A number of meters to over ten meters.

15-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Mounted Reader

5-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Mounted Reader

UHF 12-dBi RFID Antenna ISO 18000-6C


RFID Antenna UHF
15-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
UHF Tag
4″x2″ 860-960MHz UHF RFID Label RFID M4D
UHF Tag
4″x4″UHF RFID Label Alien H3 | ISO18000-6C
RFID Antenna UHF
5-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 1K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 4K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight C
HF Tag
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight EV1
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag ATA5577
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4200
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4305
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID TAG 213