
Image this: a employee in a glossy, trendy workplace constructing. They simply must faucet their RFID card in opposition to the reader, and bam! The door swings open, due to the entry management system robotically recognizing them. This tremendous handy contactless identification methodology is all made doable by HF RFID know-how. As RFID is used increasingly all over the place, it’s changing into essential in all kinds of fields, particularly for entry management and cost programs.
Now, what’s driving HF RFID? It’s all about totally different protocols, like ISO/IEC 14443 and ISO/IEC 15693. These protocols lay out the bottom guidelines for a way RFID tags and readers talk with one another. On this piece, we’ll dive into the options and makes use of of those protocols and shine a lightweight on their significance on the planet of recent RFID tech.

HF RFID Protocols Overview
Primary Rules and Options of HF RFID
How HF RFID Works
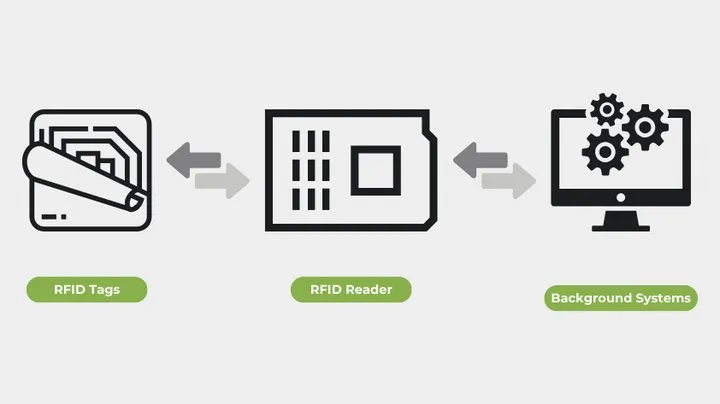
A typical HF RFID ( Excessive-Frequency Radio-Frequency Identification) system consists of three parts: RFID tags (or “playing cards”), RFID readers, and an information processing system. Every RFID tag has a chip and antenna for knowledge storage, whereas the reader communicates with the tag via radio waves to retrieve the saved data. The information processing system then processes that knowledge.
Excessive-frequency RFID operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz and sometimes makes use of passive tags that don’t want batteries. These tags harness power from the electromagnetic waves emitted by the reader to mirror alerts and ship again knowledge.
Options of HF RFID
Sturdy Safety: HF RFID programs help sturdy encryption and authentication strategies to make sure safe knowledge transmission. Particularly in functions like cost programs and entry management, RFID protocols can use advanced encryption algorithms to maintain data safe from theft.
Good Compatibility: HF RFID know-how presents sturdy compatibility throughout units. With standardized protocols (like ISO/IEC 14443, ISO/IEC 15693), units from totally different producers sometimes work seamlessly collectively, guaranteeing interoperability throughout programs.
Quick and Handy: HF RFID permits fast knowledge alternate, normally finishing recognition and knowledge switch in simply milliseconds. This effectivity makes RFID nice for conditions needing a speedy response, like visitors funds and identification checks.
Contactless: Not like old-school barcodes or magnetic stripe playing cards, RFID tech doesn’t require bodily contact for knowledge alternate. Customers simply must carry the RFID tag close to the reader to switch data, enhancing consumer expertise and minimizing put on.
Key Elements of RFID Protocols
Knowledge Encoding and Modulation Methods
To make sure a easy knowledge transmission between RFID tags and readers, high-frequency RFID protocols make the most of particular encoding and modulation methods. Frequent modulation strategies embody:
ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying): Adjustments in sign amplitude to characterize totally different binary knowledge.
PSK (Part Shift Keying): Alters the section of the sign to ship knowledge.
Knowledge encoding strategies additionally guarantee dependable data switch in noisy environments. Completely different protocols (like ISO/IEC 14443 and ISO/IEC 15693) use varied encoding schemes to attain one of the best sign transmission high quality.
Communication Protocols
The primary position of RFID communication protocols is to make sure that tags and readers can efficiently and securely alternate knowledge. Sometimes, high-frequency RFID protocols embody a number of key steps:
Modulation and Demodulation: The RFID tag modulates knowledge onto radio waves, and the reader demodulates it to retrieve the unique data.
Backscatter: In battery-free passive tags, the reader prompts the tag utilizing electromagnetic waves, which the tag then makes use of to ship data again through backscatter.
Knowledge Handshake: Earlier than beginning communication, the tag and reader initialize and confirm readiness to make sure each are set for knowledge switch.
Feathers and Functions of 5 Frequent HF RFID Protocols
HF RFID know-how entails varied protocol requirements tailor-made to particular use instances. Frequent HF RFID protocols embody ISO/IEC 14443, NFC, ISO/IEC 15693, ISO/IEC 18000-3, and FeliCa. Every protocol has its distinct traits and acceptable functions understanding these variations and benefits aids in choosing the proper RFID know-how answer.
ISO/IEC 14443 Protocol
ISO/IEC 14443 is a well-liked near-field RFID protocol generally utilized in high-security conditions requiring short-range communication. Operating within the 13.56 MHz frequency space, this protocol is ideal for functions needing exact location monitoring and tight knowledge safety. It is available in two varieties:
Kind A: Produced by firms like NXP, it finds vast use in cost playing cards and identification checks.
Kind B: Developed by Sony and different companies, it has a robust presence in Europe and components of Asia, usually seen in digital passports.
Examples of chips embody MIFARE Traditional®, MIFARE® DESFire®, and I-Code, that are broadly adopted throughout varied RFID programs, offering stable safety and ample storage capability.
Key Options
Communication Vary: The ISO/IEC 14443 protocol usually operates inside a communication distance of 0-10 cm, making it appropriate for functions the place very shut proximity and excessive safety are essential. This quick distance is efficient in averting distant threats, guaranteeing interactions solely happen when objects or persons are close to the reader.
Knowledge Switch Velocity: This protocol is able to high-speed transmission, as much as 848 kbps, facilitating swift knowledge transfers. Thus, ISO/IEC 14443 excels in functions that demand fast processing, similar to cost transactions and identification verification operations.
Functionality for Multi-tag Studying: ISO/IEC 14443 normally can not learn a number of tags concurrently. As a result of its restricted vary and heightened safety necessities, programs sometimes course of every tag one by one to take care of knowledge accuracy and safety.
Benefits
Excessive Safety: ISO/IEC 14443 protocols usually implement encryption methods (like DES, 3DES, AES) to safeguard knowledge, stopping unauthorized entry or breaches.
Fast Switch Charge: It helps quick knowledge switch to accommodate the calls for of high-speed transactions and identification checks.
Established Market Use: It’s broadly utilized in essential sectors like funds and identification affirmation, with quite a few real-world examples.
Utility Situations
Contactless Cost Programs: Playing cards like Visa PayWave and MasterCard PayPass permit customers to easily maintain their playing cards close to the cost terminal to rapidly deal with transactions.
Identification Verification Functions: ISO/IEC 14443 is usually utilized for digital passports, good IDs, campus playing cards, and entry management programs, enabling swift consumer identification checks via RFID tags.
Public Transport Funds: In instances like bus and subway playing cards, passengers simply want to carry their playing cards close to the reader for fast cost processing, providing a streamlined public transport expertise.

NFC Protocol
NFC (Close to Discipline Communication) is a short-range communication know-how primarily based on the ISO/IEC 14443 protocol, usually used for fast knowledge exchanges between smartphones and different units. It’s significantly helpful for cell funds, gadget pairing, and digital ticketing, with widespread chip varieties like NXP PN532, Sony FeliCa, and Broadcom BCM2079 present in smartphones and wearables.
Key Options
Communication Distance: NFC operates at a really quick vary, normally not more than 4 centimeters, guaranteeing safe and personal knowledge transfers. This limits pointless long-distance communication whereas permitting speedy, steady exchanges.
Knowledge Switch Charge: NFC helps low switch charges, sometimes between 106 kbps to 424 kbps, greatest for small knowledge transactions. This charge matches properly with its major makes use of in authentication and funds.
Multi-Tag Studying: Usually, NFC doesn’t help studying a number of tags without delay. It’s designed for direct, one-on-one communication, guaranteeing accuracy and safety with every knowledge alternate.
Advantages
Two-Approach Communication: NFC permits units to ship and obtain knowledge, making it versatile for pairing and authentication duties.
Quick Interplay: NFC connections are practically prompt; merely carry units shut for fast knowledge swaps, enhancing consumer comfort.
Low Energy Use: In comparison with different wi-fi tech, NFC makes use of much less energy, making it ultimate for battery-powered units like smartphones.
Utility Situations
Cell Funds: NFC is integral to companies like Apple Pay and Google Pay, enabling customers to make fast transactions by merely putting their cellphone close to a cost terminal.
Machine Pairing: It facilitates quick connections between good units and wearables, similar to Bluetooth headphones or smartwatches, by permitting customers to only carry units collectively.
Digital Ticketing: NFC additionally streamlines how customers validate tickets for occasions, letting them merely maintain their telephones or NFC playing cards as much as a reader for fast entry.

ISO/IEC 15693 Protocol
ISO/IEC 15693 is one other widespread high-frequency RFID protocol that helps longer communication distances (sometimes as much as 1 meter) in comparison with ISO/IEC 14443. It’s designed for functions the place knowledge switch charges are usually not as important. This makes it ultimate for stock administration and monitoring as a result of its decrease value and higher flexibility. Frequent chip varieties embody I-Code SLI, TI Tag-it, and Philips I-Code, which are sometimes utilized in areas similar to asset administration and logistics monitoring.
Key Options
Communication Distance: ISO/IEC 15693 has an extended communication vary, sometimes as much as 1 meter, permitting for extra intensive learn/write operations in comparison with the 0-10 cm vary of ISO/IEC 14443. This function makes it significantly fitted to much less safe environments that require a broader scanning vary.
Knowledge Switch Charge: With a most knowledge switch charge of 26.4 kbps, ISO/IEC 15693 is comparatively gradual. This limitation makes it higher fitted to situations that require solely small quantities of knowledge alternate or the place real-time switch isn’t important, enhancing its effectiveness for functions that want steady monitoring of quite a few objects.
Multi-tag Studying Functionality: This protocol usually permits multi-tag studying; nevertheless, dense environments can hinder its efficiency. It demonstrates higher efficiency than ISO/IEC 14443 in relation to dealing with a number of tags however should still require optimization to spice up effectivity.
Benefits
Prolonged Learn/Write Distance: With the flexibility to achieve as much as 1 meter, ISO/IEC 15693 is ideal for functions that must learn tags from a distance.
Value-Effectiveness: Compared to different HF RFID protocols, ISO/IEC 15693 is usually cheaper, making it a extra sensible choice for widespread deployment.
Perfect for Massive-Scale Merchandise Administration: Its longer learn vary makes it exceptionally well-suited for asset monitoring and stock administration, permitting for speedy scanning of a number of objects throughout bigger areas.
Utility Situations
Asset Administration: Warehouse administration, tools monitoring, and stock administration steadily make use of ISO/IEC 15693. RFID tags allow programs to rapidly establish and find belongings, thereby lowering the workload related to guide counts and enhancing administration effectivity.
Logistics Monitoring: This protocol is usually utilized in cargo monitoring and provide chain administration. In logistics operations, RFID tags mark merchandise, aiding firms in monitoring the standing of shipments in real-time, guaranteeing that items are correct and well timed.
Library Administration: Inside library administration programs, ISO/IEC 15693 helps streamline the borrowing and returning of books. As soon as connected, RFID tags permit the system to robotically retrieve e book data, lowering guide work and enhancing general library operations.

ISO/IEC 18000-3 Protocol
ISO/IEC 18000-3 is a section of the ISO/IEC 18000 collection of requirements designed for HF RFID units. This normal operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz and presents a standardized protocol aimed toward selling interoperability between varied RFID units. It primarily targets RFID functions like asset administration and provide chain monitoring. Frequent chip varieties embody TI Tag-it and Impinj Monza, which permit for various functions and allow environment friendly knowledge exchanges.
Key Options
Communication Distance: ISO/IEC 18000-3 sometimes presents a communication vary much like ISO/IEC 15693, reaching round 1 meter. Its standardized design permits it to adapt to totally different environments and {industry} calls for, offering flexibility and compatibility throughout varied functions.
Knowledge Switch Charge: This protocol helps a number of knowledge switch charges to suit totally different utility wants. You may select and modify the charges primarily based on particular functions, optimizing efficiency throughout various operational settings and facilitating knowledge transactions starting from low to excessive speeds.
Multi-tag Studying Functionality: ISO/IEC 18000-3 protocols help multi-tag studying, which is very useful for large-scale asset administration, warehousing, and logistics operations. This function permits programs to acknowledge and course of a number of RFID tags concurrently, enhancing each effectivity and pace.
Benefits
Standardized Protocol: Being one of many vital requirements within the RFID sector, ISO/IEC 18000-3 delivers a constant technical framework that facilitates interoperability amongst totally different units and programs. Whether or not in native or international markets, RFID units using ISO/IEC 18000-3 can obtain compatibility throughout manufacturers and platforms.
Flexibility for Cross-industry Functions: The design of the protocol lends itself effectively to broad utility throughout varied sectors, masking every part from logistics administration to medical gadget monitoring whereas providing constant efficiency and reliability for various RFID wants.
Help for Environment friendly Multi-tag Learn/Write: For expansive functions, ISO/IEC 18000-3 can help a number of tags studying, enhancing operational effectivity considerably, making it ultimate for high-throughput situations.
Utility Situations
Asset Administration and Stock Management: Sectors similar to retail, logistics, and warehouse administration extensively apply ISO/IEC 18000-3. With RFID know-how, companies can swiftly and precisely monitor the standing and placement of stock objects, bolstering stock administration effectivity and minimizing guide counting efforts.
Provide Chain Administration: Within the realm of provide chain administration, ISO/IEC 18000-3 establishes knowledge alternate requirements between units, fostering transparency and real-time data circulate. This functionality permits companies to maintain tabs on the delivery standing of every merchandise, guaranteeing complete monitoring and optimization of the product journey from manufacturing to supply.

FeliCa Protocol
FeliCa is an RFID protocol designed by Sony that operates on a 13.56 MHz frequency, primarily utilized in Japan and different components of the Asia-Pacific area. This protocol builds on the ISO/IEC 14443 normal, enhancing it particularly for cost programs and transit administration. FeliCa presents excessive safety, quick communication, and dependable knowledge alternate, making it a well-liked selection in finance and public transport. Frequent chip examples embody Sony FeliCa and RC-S960, which discover intensive use in cost and transit playing cards.
Key Options
Communication Distance: Sometimes, FeliCa operates at a distance of 0-10 cm, making it good for situations requiring fast knowledge alternate, like funds and ID verification. This quick vary boosts safety by minimizing the chance of distant knowledge breaches or interference.
Knowledge Switch Charge: FeliCa helps excessive switch charges of as much as 424 kbps, enabling quick dealing with of cost and ID verification duties, which is important for situations with frequent knowledge exchanges.
Multi-Tag Studying: This protocol permits for multi-tag studying, appropriate for environments that require simultaneous processing of a number of tags. A number of FeliCa playing cards might be learn collectively, reducing down on ready time and enhancing effectivity.
Benefits
Strong Safety and Encryption: FeliCa employs encryption and safety mechanisms (like DES and AES) to guard knowledge, lowering the dangers of counterfeiting and knowledge leaks.
Quick Knowledge Alternate: With speeds reaching 424 kbps, FeliCa facilitates fast cost and ID verification processes, catering to environments the place speedy exchanges are important.
Different Functions: FeliCa has seen broad adoption in public transit and cost programs, gaining favor for its effectivity and safety amongst customers and companies alike.
Utility Situations
Public Transport: In Japan, FeliCa tech powers transportation playing cards like Suica and Pasmo. Customers can simply pay for buses and trains simply by holding their playing cards or telephones close to a reader, streamlining the journey cost course of.
Digital Wallets: FeliCa can be broadly utilized in digital wallets and cost apps like Edy and QUICPay. Customers outfitted with FeliCa-enabled units (like good playing cards and smartphones) can take pleasure in quick transactions, making buying and funds fast and hassle-free.
Entry Management: Entry management programs implement FeliCa, utilizing it extensively in places of work and faculties for identification verification. It permits customers to swiftly confirm their identities at entry factors utilizing FeliCa playing cards or smartphones to realize entry to safe areas.

Future Tendencies and Challenges for HF RFID Protocol
Technological Advances
Merging IoT and 5G Applied sciences: As IoT and 5G applied sciences maintain advancing, using HF RFID protocols is ready to broaden throughout varied industries. As an example, in good properties, RFID can hyperlink up with good units to facilitate computerized identification and administration of things. In autonomous driving situations, RFID tags may allow environment friendly communication between autos and automate cost processes. The mix of those applied sciences is anticipated to spice up the effectivity of RFID protocols and unlock modern functions throughout a number of sectors.
Elevated Safety: Transferring ahead, RFID protocols are more likely to function enhanced safety functionalities, particularly round knowledge transmission security. With developments in quantum encryption applied sciences, RFID programs might incorporate quantum cryptographic algorithms to bolster knowledge safety and defend in opposition to potential assaults and knowledge theft. This shall be essential in delicate functions like funds and identification verification.
Challenges and Boundaries
Frequency Interference Points: Though the HF RFID band (13.56 MHz) is broadly employed, its alerts might be simply disrupted by electromagnetic interference. That is significantly true in sure industrial environments or places crowded with digital units, which might compromise the steadiness of RFID communication. To take care of dependable RFID programs, future developments might require sturdy anti-interference applied sciences and protocol optimizations to deal with advanced environments.
Standardization and Compatibility Issues: Regardless of the broad adoption of RFID know-how worldwide, the development of standardization stays a problem. Compatibility points between varied RFID protocols (like ISO/IEC 14443 and ISO/IEC 15693) nonetheless persist, probably hindering cross-device and cross-sector functions. Completely different merchandise from varied producers might fit discrepancies, and divergent international requirements can complicate know-how convergence. Thus, fostering unified standardization throughout the {industry} and enhancing interoperability amongst protocols shall be important for the longer term progress of RFID know-how.

Conclusion
The HF RFID protocol is tremendous essential for wi-fi communication and knowledge swapping these days. Particular protocols like ISO/IEC 14443, NFC, ISO/IEC 15693, ISO/IEC 18000-3, and FeliCa all have their very own distinctive makes use of in several conditions. Selecting the best protocol actually relies on what you want, like how far you wish to talk, how briskly you wish to switch knowledge, how safe you want it to be, and if you wish to learn a number of tags without delay. So, companies and industries ought to choose the fitting RFID protocol in keeping with their very own must maintain their programs operating effectively and reliably.
Seeking to the longer term, applied sciences like IoT and 5G will maintain spreading using HF RFID protocols, particularly in scorching areas like good properties, self-driving automobiles, and good manufacturing. As these applied sciences develop, we’ll see HF RFID protocols utilized in additional methods, opening up recent alternatives for innovation. Plus, issues like safety, stability, and compatibility of those protocols will maintain getting higher to deal with the extra advanced {industry} calls for and tech challenges. With steady enhancements and inventive developments, HF RFID protocols will play an enormous position in pushing digital and good transformations all around the globe.
For those who’re curious to study extra about NFC and RFID, try rfidltd.com!

FAQs
What are the variations between HF RFID and LF RFID?
HF RFID (Excessive-Frequency RFID) and LF RFID (Low-Frequency RFID) have some clear variations in relation to frequency vary, communication distance, utility situations, and efficiency:
Frequency Vary: HF RFID normally operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, whereas LF RFID runs at both 125 kHz or 134.2 kHz.
Communication Distance: HF RFID sometimes has a communication vary of 0-1 meter, however LF RFID has a shorter vary, normally just some centimeters to a number of tens of centimeters.
Knowledge Switch Velocity: HF RFID helps increased knowledge switch speeds, usually reaching as much as 848 kbps, whereas LF RFID’s charges are decrease, sometimes between 1-10 kbps.
Utility Situations: HF RFID is nice for functions needing medium-range communication and excessive knowledge switch speeds, like contactless funds and asset administration. LF RFID, nevertheless, is normally used for short-distance functions, similar to animal monitoring and entry management.
Can ISO/IEC 14443 and ISO/IEC 15693 be used collectively?
ISO/IEC 14443 and ISO/IEC 15693 are two totally different RFID protocols that aren’t totally appropriate as a result of they’ve totally different designs and working ideas. Though each are high-frequency RFID requirements working at 13.56 MHz, they range in knowledge switch pace, communication distance, and utility situations.
ISO/IEC 14443 is especially for short-range, high-speed knowledge exchanges and is greatest for functions that require excessive safety, like cost programs and identification verification. On the flip aspect, ISO/IEC 15693 fits longer communication distances (as much as 1 meter) however presents decrease switch speeds, making it ultimate for asset administration and logistics monitoring. So whereas they each use the identical frequency band, their protocols and units aren’t immediately appropriate. If it’s good to use totally different protocol tags in the identical system, you sometimes want separate readers to help each.
What components can intervene with RFID protocols?
Just a few components can intervene with RFID protocols, particularly HF RFID protocols.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): In some industrial settings, giant equipment, electrical units, or wi-fi sign sources can create sturdy electromagnetic interference that messes with the communication between RFID tags and readers.
Metals and Liquids: Metals and liquids can disrupt RFID sign transmission, significantly in high-frequency RFID functions. Metallic surfaces can bounce RFID alerts, whereas liquids might take in electromagnetic waves, inflicting sign loss and negatively impacting communication distance and stability.
Tag Density: When there are a variety of RFID tags in the identical space, it will probably result in sign collisions or points with studying a number of tags, affecting how effectively and precisely the system works.
Environmental Noise: Noise from different digital units or crowded wi-fi frequency bands also can make RFID alerts unstable or trigger them to be misplaced.
Rec-Merchandise

BioPoly™ Stone Intercontinental Accommodations & Resorts Key Card

PVC Intercontinental Accommodations & Resorts Key Card

Picket Intercontinental Accommodations & Resorts Key Card


RFID Antenna UHF
15-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
UHF Tag
4″x2″ 860-960MHz UHF RFID Label RFID M4D
UHF Tag
4″x4″UHF RFID Label Alien H3 | ISO18000-6C
RFID Antenna UHF
5-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 1K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 4K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight C
HF Tag
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight EV1
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag ATA5577
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4200
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4305
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID TAG 213