With the speedy growth of contemporary expertise, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags have change into a major drive driving progress throughout varied sectors. Whether or not in enterprise logistics, provide chain administration, or good merchandise monitoring in on a regular basis life, these tags play an indispensable function. These small units not solely enhance operational effectivity but in addition improve information administration and safety, bringing substantial adjustments to our world.
RFID tags are the core element of RFID expertise. They convert advanced radio alerts into readable information, making the acquisition and processing of knowledge extra environment friendly and correct. Via these tags, we will obtain real-time monitoring of things, optimize useful resource allocation, and scale back human errors.
On this weblog, we’ll take a deep dive into the working ideas of RFID tags, revealing their inside construction and creation course of that will help you totally perceive how this vital expertise impacts our day by day lives and enterprise operations.
How RFID Tags Work
Communication between RFID tags and readers is completed via radio waves. The RFID reader emits radio frequency waves that the tag’s antenna picks up. This triggers the tag’s microchip to activate, which then transmits the saved information again to the reader through the antenna. This data usually features a distinctive identifier or different related information. The reader receives this data, decodes it, and eventually transmits the info to the backend system for processing.
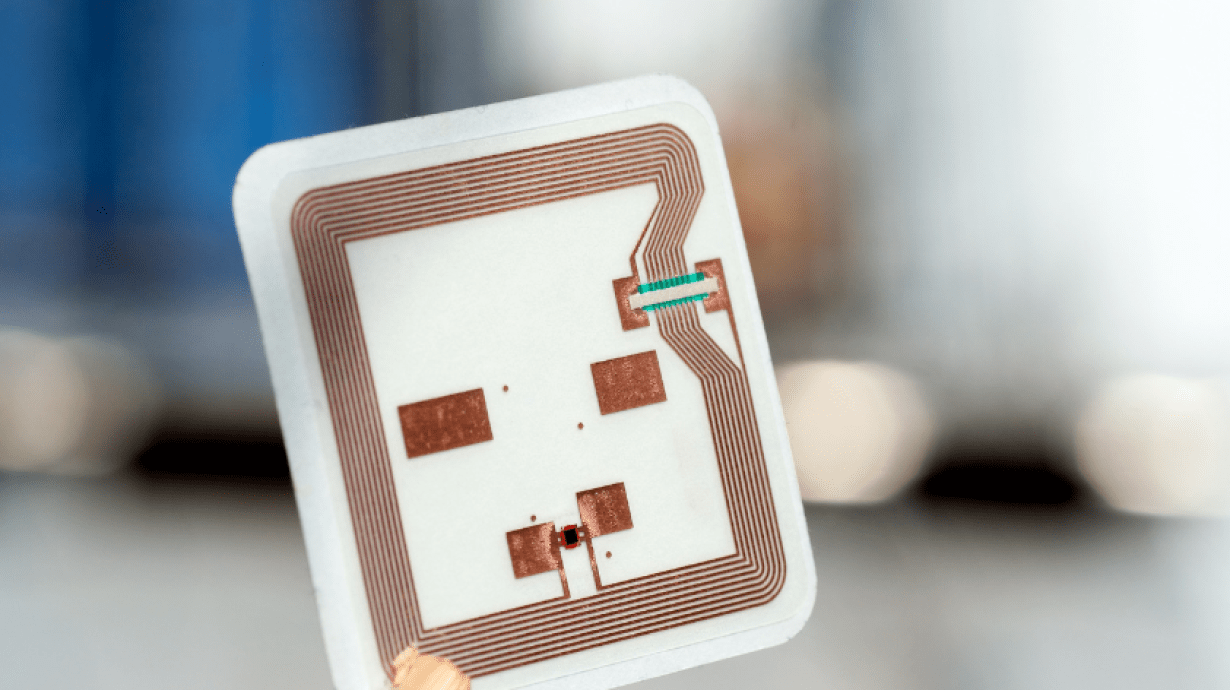
Fundamental Elements of RFID Tags
The fundamental elements of RFID tags embrace:
Antenna
The antenna of the RFID tag is accountable for receiving and sending radio waves to speak wirelessly with the RFID reader. The design and materials of the antenna straight have an effect on the studying distance and efficiency of the tag. Widespread antenna sorts embrace printed antennas, patch antennas, and loop antennas. The supplies used for the antenna are normally copper or aluminum as a consequence of their wonderful conductive properties.
Microchip (Built-in Circuit)
The microchip serves because the central management unit of the RFID tag, managing the storage and processing of knowledge. The chip comprises a microprocessor, reminiscence, and a wi-fi communication module. Its foremost operate is to retailer distinctive identification data and alternate information with the reader via the antenna. Design necessities for the microchip embrace miniaturization, excessive effectivity, and low energy consumption.
Substrate
Because the supporting materials for the RFID tag, the substrate is usually manufactured from plastic, paper, or artificial supplies. Its foremost operate is to offer structural help whereas defending the inner antenna and microchip. The selection of substrate materials straight impacts the sturdiness and environmental adaptability of the tag. For purposes requiring excessive temperature resistance or waterproofing, the substrate materials should have the suitable traits.
RFID Tag Manufacturing Course of
Step 1: Design and Preparation
The manufacturing means of RFID tags begins on the design stage. Designers want to find out the dimensions, form, working frequency, and efficiency indicators of the tag primarily based on precise software necessities. Throughout this design course of, it’s vital to contemplate the tag’s working setting, comparable to whether or not it must be waterproof, heat-resistant, or immune to interference. As soon as the design is finalized, producers will produce antennas and microchips in line with the design specs.
Step 2: Integration of Microchips and Antennas
Integration is a key step in manufacturing RFID tags. At this stage, the microchip is mounted onto the antenna to type an RFID module. This course of normally entails soldering the microchip to the antenna. The mixing of the antenna and microchip requires excessive precision to make sure the steadiness and reliability of the sign. After integration, the RFID module is hooked up to the substrate.
Step 3: Testing and Packaging of Tags
As soon as integration is full, the RFID tag undergoes rigorous testing to make sure its efficiency meets requirements. These exams embrace studying distance, information transmission pace, and interference resistance. After passing the exams, the tag is encapsulated to guard its inside elements. The packaging materials usually features a plastic casing and a metallic shielding layer to boost the tag’s sturdiness and resistance to interference.
RFID Tag Utility Fields
RFID tags are extensively utilized in many industries, comparable to:
Retail Trade
The appliance of RFID tags in retail is primarily seen in stock administration and anti-theft programs. Retailers like Zara and Uniqlo use RFID expertise to trace stock and forestall theft. These tags not solely replace stock information in real-time but in addition improve the client expertise by enhancing stock accuracy. Retailers can shortly find items and scale back stock backlogs.
Logistics Trade
In logistics, RFID tags are used for monitoring and managing items. By attaching RFID tags to every cargo, logistics corporations can monitor the transportation standing and site of products in real-time. This performance tremendously enhances provide chain visibility and streamlines operations, minimizing the probability of delays and losses. Corporations like Walmart and Dell have optimized their provide chain administration utilizing RFID expertise.
Medical Trade
Within the medical discipline, RFID tags are utilized to trace medical units and medicines. Hospitals use RFID tags to make sure correct gear location, scale back errors, and improve affected person security. For example, by utilizing RFID tags on medicine packaging, hospitals can guarantee appropriate distribution and monitoring of medication, thereby minimizing medicine errors.
Future Outlook of RFID Tags
As expertise continues to advance, the features and software areas of RFID tags are additionally increasing. Future RFID tags could combine extra clever features, comparable to temperature monitoring and environmental sensing, enabling them to play a job in a wider vary of purposes. For instance, good packaging could use RFID expertise to observe the environmental situations of merchandise, comparable to temperature and humidity, to make sure product high quality.
FAQ
1.During which industries are RFID tags most generally used?
They extensively use RFID tags in retail, logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing. These industries use RFID expertise to enhance operational effectivity, scale back errors, and optimize useful resource administration.
2.How do RFID tags work?
They use radio waves to work together with readers, sending the info saved within the tags over to them. The readers seize these alerts, interpret the info, and finalize the method of retrieving and processing the data.
3. What are the sorts of RFID tags?
The three foremost sorts are passive tags, lively tags, and semi-active tags. Passive tags do not need built-in batteries and depend on power supplied by the reader to function; lively tags have built-in batteries and may work over longer distances; semi-active tags have batteries however nonetheless depend on the reader’s power to activate.
Rec-Merchandise

Built-in UHF RFID Reader
The built-in UHF RFID reader is a single-channel mounted UHF RFID reader, which is provided with an built-in high-performance antenna primarily based on the self-developed module primarily based on the Impinj E710 chip. It helps a number of communication interfaces comparable to RS-232, RJ45, GPIO, and so on., enabling it to be extensively utilized in a number of situations comparable to warehousing, file administration, e book administration, banking, and manufacturing line administration.

Multi-Protocol Desktop HF RFID Reader
Desktop HF RFID Reader AZ-RL863 is a high-performance, multi-functional 13.56 MHz Excessive-frequency RFID desktop reader designed for situations that require steady and efficient RFID information interplay. It helps the mainstream HF protocols of ISO/IEC 14443A, 14443B , 15693, 18000-3, and is appropriate with a wide range of tag sorts, and might be extensively utilized in desktop card issuance, entry management, e-tickets, fee terminals, e book lending programs and different fields.

15-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fastened Reader
RP-TNC male- N male, for U300 with 9-12dBi antenna, 15 meters

5-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fastened Reader
RP-TNC male – SMA male, for U300 with 5dBi antenna, 5 meters

RFID Antenna UHF
15-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
UHF Tag
4″x2″ 860-960MHz UHF RFID Label RFID M4D
UHF Tag
4″x4″UHF RFID Label Alien H3 | ISO18000-6C
RFID Antenna UHF
5-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 1K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 4K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight C
HF Tag
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight EV1
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag ATA5577
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4200
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4305
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID TAG 213