
Ever tapped your phone to pay or breezed through inventory checks with a scanner? You’ve likely encountered NFC or RFID. While often mentioned together, Near Field Communication (NFC) and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) aren’t the same. They’re distinct technologies powering countless interactions, from seamless mobile payments to robust RFID supply chain solutions.
Think of them as cousins in the wireless world – related, but with unique talents. Understanding their differences is key to leveraging their power. Let’s dive into what sets NFC and RFID apart, how they work together, and which might be the right fit for your business needs, whether you’re looking for bulk NFC tag suppliers or comprehensive RFID asset tracking systems.
1. RFID Explained: The Magic of Radio Waves in Identification
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a powerhouse for automatic identification. It uses radio waves to identify and track objects equipped with special tags. Think of it as a wireless barcode, but much smarter, enabling real-time tracking and management without needing a direct line of sight – a cornerstone for modern inventory management solutions.
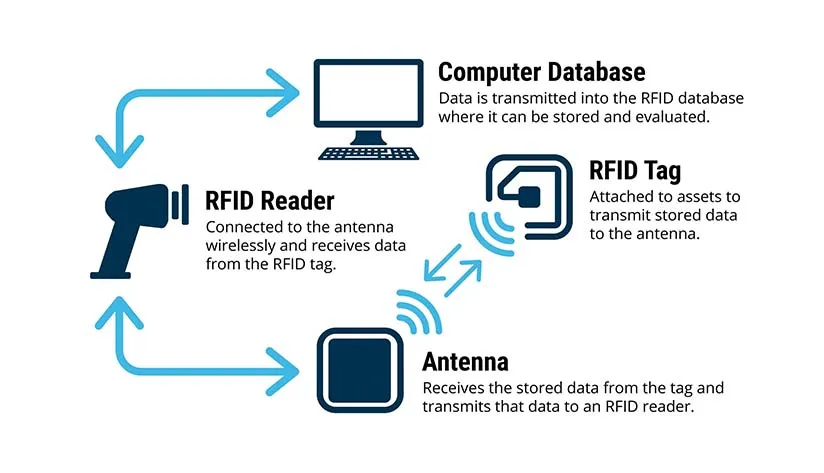
The Building Blocks of an RFID System
An RFID setup typically involves:
- RFID Tags: Tiny transmitters with chips and antennas, storing data about the item they’re attached to. Options range from simple passive tags to sophisticated custom RFID tags for specific applications.
- RFID Readers: Devices that send out radio signals to activate tags and receive their data. Choosing the right RFID reader hardware depends on range and environment.
- Backend System: The software brain that processes, analyzes, and stores the data collected by the readers.
How Does RFID Actually Work?
It’s a rapid-fire conversation: The reader sends out a radio signal. Any compatible RFID tag within range picks up this signal, powers its chip (if passive), and sends back its stored information via its antenna. The reader captures this data and passes it to the backend system. This entire exchange happens in less than a second, enabling incredible efficiency.
Where You’ll Find RFID in Action
RFID technology is revolutionizing various sectors:
- Retail Revolution: Used for sharp RFID inventory management, reducing shrinkage, and speeding up checkout.
- Logistics & Supply Chain: Essential for tracking goods from warehouse to delivery, optimizing routes, and ensuring visibility with robust logistics tracking solutions.
- Asset Tracking: Businesses use RFID asset tracking to monitor valuable equipment, tools, and vehicles, preventing loss and improving utilization. Consider the cost of implementing RFID asset tracking for ROI calculations.
- Security & Access Control: Powers key fobs, ID badges, and toll passes for secure, contactless entry.
Active vs. Passive RFID: What’s the Difference?
RFID tags come in two main flavors:
- Active Tags: Have their own battery, enabling them to broadcast signals over longer distances (tens of meters). Ideal for high-value asset tracking but come at a higher active RFID tag price.
- Passive Tags: No battery; they draw power from the reader’s signal. Shorter range (up to ~10-15 meters) but significantly cheaper, making them perfect for large-volume applications like retail tagging. Many passive RFID tag manufacturers offer diverse options.
2. NFC Unpacked: Close-Range Communication Simplified
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a specialized subset of RFID technology, designed for very short-range wireless data exchange – we’re talking centimeters. This proximity requirement is its superpower, enabling secure and intuitive interactions. Think of the tap-to-pay function on your phone – that’s NFC, often utilizing secure NFC chips for payment.
NFC interactions usually involve an active device (like your smartphone or a POS terminal) and a passive target (an NFC tag, sticker, or card). Its “touch-and-go” nature makes it incredibly user-friendly for quick, secure tasks.

Everyday NFC Applications
NFC has seamlessly integrated into daily life:
- Mobile Payments: The driving force behind Apple Pay, Google Pay, and other contactless payment systems. Essential for businesses seeking modern NFC point-of-sale solutions.
- Contactless Access: Used in transit cards, hotel key cards, office badges, and event passes for quick, secure entry. Explore NFC access control systems for businesses.
- Smart Devices & IoT: Simplifies pairing Bluetooth devices, configuring smart home gadgets, or triggering actions just by tapping your phone to an NFC smart tag.
- Information Sharing: Embedded in posters, products, or NFC business cards to instantly share websites, contact details, or app links.
3. NFC vs. RFID: The Key Distinctions
While related, NFC and RFID have crucial differences influencing their best use cases. Choosing the right RFID or NFC solution provider depends on understanding these.
Reach: How Far Do They Go?
This is the biggest differentiator. RFID, especially active RFID, can operate over many meters. Passive RFID reaches up to around 10-15 meters. NFC? It’s strictly close-quarters, typically 4 cm or less. This makes RFID ideal for warehouse scanning and NFC perfect for secure transactions where proximity is key.
Frequency & Speed: The Tech Specs
RFID operates across Low (LF), High (HF), and Ultra-High (UHF) frequencies, each suited for different applications. NFC operates *only* at the HF frequency of 13.56 MHz. This shared frequency means NFC devices can often read HF RFID tags. NFC generally offers faster data transfer initiation for quick interactions like payments (up to 424 kbps), while RFID speeds vary by type and frequency.
Power Play: Battery vs. Borrowed Energy
Active RFID tags need batteries, adding cost and maintenance but enabling long range. Passive RFID and all NFC tags are typically passive, drawing power from the reader/initiator device. This makes passive RFID and NFC tags cheaper and maintenance-free, ideal for high-volume, disposable uses or embedding in devices like smartphones.
4. The Symbiotic Relationship: How NFC and RFID Connect
NFC isn’t just a short-range RFID; they often work together, complementing each other’s strengths.
Built on RFID Foundations
NFC technology evolved from RFID standards, specifically operating within the HF RFID spectrum (13.56 MHz). This shared heritage allows for interoperability – an NFC-enabled smartphone can often read HF RFID tags, bridging the gap between large-scale tracking and consumer interaction.

Working Together Across Industries
Combining these technologies unlocks powerful solutions:
- Smarter Logistics: Use RFID for long-range pallet tracking in the warehouse and NFC via a smartphone app for final delivery confirmation or detailed item checks. A complete track and trace solution.
- Enhanced Retail Experience: RFID tracks inventory efficiently. Customers can then use NFC on their phones to tap product tags (NFC product tags) for more info, reviews, or even add-to-cart functionality.
- Layered Security: An RFID badge might grant building access, while NFC on a phone could be required for access to high-security areas or specific equipment.
NFC: The User-Friendly Interface for RFID Data
With most smartphones now NFC-enabled, NFC acts as a convenient bridge for users to interact with the world of RFID. Tapping an RFID-tagged library book with an NFC phone could instantly bring up borrowing options or reviews. This capability turns passive data sources into interactive experiences, driving demand for integrated RFID and NFC system integration services.
5. Real-World Wins: NFC & RFID Integration Success Stories
The synergy between NFC and RFID (often both using the 13.56 MHz frequency for compatibility) is creating tangible benefits across industries.
Seamless Payments Powering Commerce
Contactless payment is a prime example. Your credit card likely has an RFID chip (passive HF) storing payment details securely. Your phone uses NFC to emulate that card or communicate directly with the NFC payment terminal. This combination offers speed for the consumer and robust security protocols behind the scenes.
Intelligent Retail & Warehouse Operations
Imagine a warehouse using UHF RFID portal readers for bulk inventory scans. Then, floor staff use NFC-enabled handhelds or phones to quickly verify specific item details on an HF RFID tag or update its status. This blend optimizes both large-scale visibility and granular control, reducing manual errors inherent in older systems.

Advancing Healthcare Efficiency & Safety
Hospitals use RFID tags (often HF or UHF) to track expensive mobile equipment (RFID medical equipment tracking) and manage pharmaceutical inventory. Nurses can use NFC-enabled devices to tap a patient’s RFID wristband to instantly verify identity and access medical records, improving patient safety and workflow efficiency.
Connecting the Smart Home & IoT
RFID tags can be embedded in appliances for identification and lifecycle tracking. NFC provides the user-friendly interface: tap your phone to an NFC tag on your smart thermostat to open its control app, or tap a tag on your washing machine to download the correct cycle settings. This makes interacting with the growing Internet of Things intuitive.
6. Weighing the Options: Pros and Cons of NFC & RFID
Choosing between NFC and RFID solutions, or deciding to integrate both, requires understanding their inherent strengths and weaknesses.
Why Choose NFC? (The Upsides)
- User-Friendly: Extremely simple – tap and go. Great for consumer applications.
- Fast Connection: Quick initiation for payments and data exchange.
- Low Power: Ideal for mobile devices; passive tags need no power.
- Secure (Proximity): Short range makes remote interception difficult, good for payments.
- Lower Cost Tags: Simple NFC sticker tags can be very inexpensive.
Why Choose RFID? (The Upsides)
- Versatile Range: From centimeters (HF) to many meters (UHF, Active).
- Broad Applications: Excellent for logistics, large inventories, asset tracking.
- Batch Reading: Can scan hundreds of tags almost simultaneously (especially UHF).
- Environmental Robustness: Tags can be designed to withstand harsh conditions. Find durable industrial RFID tags.
NFC: The Limitations
- Very Short Range: Useless for distance reading.
- One-to-One Reading: Typically interacts with only one tag at a time.
- Device Dependency: Requires an NFC-enabled reader/phone.
RFID: The Limitations
- System Cost: Readers, antennas, and especially active tags can be expensive. Consider the overall RFID system cost.
- Potential Interference: Signals can be blocked by metal/liquids (especially UHF).
- Security Concerns (Range): Longer range increases risk of unauthorized reads if not secured properly (encryption is key).
- Battery Life (Active): Active tags need battery maintenance/replacement.
7. Making the Call: Which Technology Fits Your Needs?
So, NFC tags or RFID tags? The best choice hinges entirely on your specific goals.
Opt for NFC If…
- You need secure, short-range interactions (payments, access control, device pairing).
- User convenience and simplicity are paramount (consumer apps, smart posters).
- You’re leveraging existing smartphone capabilities.
- The application involves one-to-one interaction.
- Cost per tag needs to be minimal for simple interactions (buy cheap NFC tags).

Opt for RFID If…
- You need to track many items over longer distances (warehouse inventory, logistics).
- Simultaneous reading of multiple tags is crucial for efficiency (batch scanning).
- Line-of-sight reading isn’t possible or practical.
- The tags need to endure harsh environmental conditions.
- You require a dedicated industrial RFID tracking system.
Consider Both If…
- You need a multi-layered system (e.g., RFID for bulk tracking, NFC for point-of-use interaction).
- You want to bridge large-scale operational tracking with consumer-facing convenience.
- Exploring comprehensive IoT solutions leveraging RFID and NFC.
Factor in your budget, the scale of deployment, required read range, environmental conditions, and security needs when making your decision. Consulting with RFID/NFC technology experts can help tailor the optimal solution.
8. Riding the Wave: The Future is Connected with NFC & RFID
In our increasingly connected world, NFC and RFID are not just buzzwords; they are fundamental technologies driving efficiency, security, and convenience. Understanding their unique strengths and potential synergies is vital for any business looking to innovate.
Whether you’re streamlining your supply chain management with RFID, enhancing customer engagement with interactive NFC tags, or securing your premises, these technologies offer powerful tools. Don’t just read about the future – start building it. Explore how tailored NFC and RFID solutions can transform your operations and create smarter experiences today.
FAQ
1. Can NFC tags be rewritten?
Yes, many NFC tags are rewritable, allowing data to be updated multiple times. This is common for programmable NFC tags used in dynamic applications like digital business cards or configurable smart posters.
2. Are NFC and RFID secure?
Security varies. NFC’s short range adds inherent physical security, but data can still be vulnerable without encryption. RFID’s longer range poses a greater risk of unauthorized reads if tags and communication aren’t properly secured using encryption and authentication protocols. Implementing robust RFID security measures is crucial.
3. Can NFC talk to multiple tags at once?
Generally, no. NFC is designed for one-to-one communication between a reader and a single tag per interaction, ensuring clarity in applications like payment.
4. What about the cost difference? NFC vs RFID Tags Price?
Simple passive NFC tags are typically very cheap, often cents per tag in bulk. Passive RFID tags (especially UHF) are also relatively inexpensive but can cost slightly more. Active RFID tags are significantly more expensive due to their batteries and complex electronics. The overall RFID system implementation cost (readers, software) is also usually higher than for basic NFC setups.

RFID Antenna UHF
15-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
UHF Tag
4″x2″ 860-960MHz UHF RFID Label RFID M4D
UHF Tag
4″x4″UHF RFID Label Alien H3 | ISO18000-6C
RFID Antenna UHF
5-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 1K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 4K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight C
HF Tag
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight EV1
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag ATA5577
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4200
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4305
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID TAG 213