
In right now’s fast-paced world of the Web of Issues and sensible identification, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) know-how is in all places—from warehousing and logistics to sensible manufacturing, and from entry management techniques to animal monitoring. But, among the many completely different frequency bands, low-frequency (LF) RFID, whereas it could appear “old-school,” hasn’t been phased out; in actual fact, it performs a necessary function in a number of crucial purposes.
Low-frequency RFID shines in conditions the place the communication vary isn’t intensive, however there’s a strict requirement for stability and flexibility to numerous environments, because of its sturdy stability and excessive resistance to interference.
Overview of How Low-Frequency RFID Works
Frequency Vary
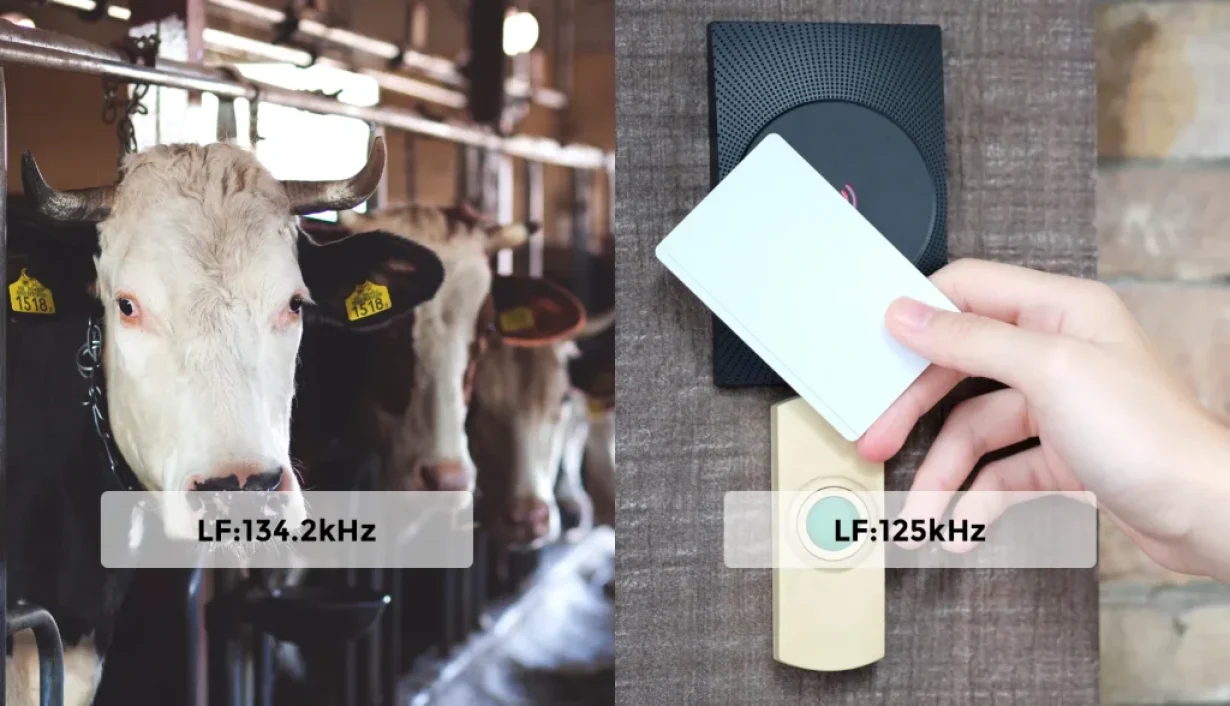
Low-frequency RFID operates inside the 30kHz to 300kHz frequency vary, with 125kHz and 134.2kHz being probably the most generally used frequencies. The 125kHz band is commonly present in entry management techniques, whereas the 134.2kHz band is usually used for animal identification (like pet and livestock chips). These frequency choices permit low-frequency RFID to perform reliably in numerous environments, notably in areas wealthy in steel or moisture.
Working Mechanism
Low-frequency RFID know-how is predicated on electromagnetic induction. Particularly, the RFID reader emits electromagnetic waves by way of its antenna, activating RFID tags inside its vary. When a tag comes into the reader’s magnetic subject, it attracts energy from the reader via induction and sends again the data saved in its chip. As a result of low-frequency RFID tags don’t require built-in batteries (they’re passive), they function very effectively and have a protracted lifespan.
Communication between the tag and reader depends on near-field inductive coupling, with typical transmission distances of 1 to 10 centimeters. The shorter transmission vary and decrease information fee of low-frequency RFID make it particularly efficient in high-security and short-distance identification purposes.
System Elements
The important thing parts of a low-frequency RFID system embrace:
LF RFID Tags: These have a storage chip and an antenna, storing a novel identifier (UID) and speaking with the reader via the antenna.
LF RFID Readers: These gadgets transmit and obtain electromagnetic waves to activate tags and skim information from them. Readers are normally linked to a management system for processing and managing information.
Management System Interface: This part connects the RFID system to different administration techniques (like entry management or attendance techniques), enabling information integration and automation.
Inductive Vary and Communication Limitations
Low-frequency RFID sometimes has a brief inductive vary, normally between 1 and 10 centimeters. Whereas this does restrict its software in large-scale logistics and long-distance monitoring, its excessive stage of safety and reliability at shut vary nonetheless make it exceptionally efficient for purposes requiring exact identification.
Key Options and Benefits of LF RFID
Sturdy Resistance to Interference
LF RFID techniques have distinctive resistance to interference in high-metal and high-moisture environments. This makes them stand out in eventualities the place electromagnetic interference is important. As an example, in lots of industrial settings, equipment and steel parts can simply disrupt RFID alerts, however the decrease frequency of LF RFID can higher penetrate these interferences, making certain the system operates easily.
Price-Efficient and Straightforward to Deploy
With years of widespread software, LF RFID know-how comes with comparatively low prices for each tools and tags. When in comparison with HF or UHF RFID techniques, LF RFID tags are cheaper to fabricate, and their set up is simple—no advanced configuration is important. This makes LF RFID a extremely cost-effective choice, particularly for small companies or organizations on a good funds.
Lengthy Lifespan and Excessive Reliability
Since LF RFID tags are passive, they don’t require batteries and are powered by the electromagnetic waves from exterior readers. This implies they’ll last as long as 10 years and even longer, considerably reducing down upkeep prices. Moreover, LF RFID presents excessive learn/write stability and is much less prone to environmental fluctuations, equivalent to modifications in temperature and humidity.
Mature Expertise with World Compatibility
LF RFID has been broadly adopted throughout numerous industries, and plenty of requirements and protocols (like ISO11784/11785) have been established and acknowledged worldwide. These requirements guarantee compatibility and interoperability amongst LF RFID gadgets, enabling customers to pick out gadgets and companies freely on a world scale.
Frequent Purposes of LF RFID
Animal Identification and Monitoring
Researchers and animal managers broadly use LF RFID in animal administration. They sometimes implant 134.2 kHz RFID tags in animals or connect them to ear tags for functions like:
Pet Identification: Microchips assist reunite misplaced pets with their homeowners.
Livestock Monitoring: Farms make use of RFID ear tags to observe the well being and breeding information of livestock.
Entry Management and Id Verification
LF is extensively utilized in entry management and id verification techniques, together with:
Workplace Buildings: Staff use RFID entry playing cards to enter workspaces.
Faculties and Hospitals: College students and employees swipe RFID playing cards to entry campuses or hospital services.
Limitations and Suitability of LF RFID
Whereas LF RFID performs exceptionally effectively in lots of conditions, it does have some limitations:
Quick Studying Distance: Due to its working precept, LF RFID sometimes has a studying vary of solely as much as 10 centimeters, making it unsuitable for large-scale logistics and long-distance computerized identification.
Low Knowledge Switch Fee: LF RFID has a comparatively gradual information switch fee, making it ultimate for figuring out low-speed objects or folks.
Restricted Knowledge Capability: LF RFID tags normally can solely retailer a small quantity of knowledge, equivalent to ID numbers, and can’t maintain intensive information.
Because of this, industries want LF RFID for eventualities that don’t require excessive studying distances and contain advanced environments. For purposes that require quicker information switch charges or long-range identification, completely different frequency bands of RFID may be obligatory.
Conclusion: LF RFID, an Previous however Trusted Expertise Selection
Due to its sturdy resistance to interference, low price, and lengthy lifespan, LF RFID remains to be a extremely dependable know-how choice in particular fields. Whether or not in animal administration or entry management, LF RFID proves to supply distinctive worth.
Now, LF RFID continues to be the go-to selection for short-range, low-speed identification wants.
FAQs
What are the Key Variations Between LF RFID and HF RFID?
The first variations between LF RFID and HF RFID are their working frequencies and transmission distances. LF RFID sometimes operates within the 125kHz or 134.2kHz vary, whereas HF RFID works at 13.56MHz. LF RFID has a shorter learn/write vary, normally only some centimeters, which makes it ultimate for short-distance purposes like entry management and animal monitoring. In distinction, HF RFID has a learn/write vary from a couple of centimeters as much as 1 meter, typically utilized in eventualities like asset administration and library administration the place longer studying distances are obligatory.
What Powers LF RFID Tags?
LF RFID tags are typically passive, that means they don’t want an inner battery for energy. As a substitute, the RFID reader emits electromagnetic waves that energy the tags. When the reader sends out these waves, the tag’s antenna picks them up, changing the alerts into electrical energy that powers the tag’s chip, enabling it to transmit information. That is why LF RFID tags typically have a protracted lifespan — they don’t drain any battery energy.
What’s the Typical Storage Capability of LF RFID Tags?
The storage capability of LF RFID tags is usually fairly small, normally only a few bytes to a number of hundred bytes. Since techniques primarily use LF RFID for identification and fundamental authentication, its storage sometimes holds a novel identification quantity (UID). In distinction, HF RFID and UHF RFID tags typically provide higher storage capacities for purposes that require extra information, like asset administration and product monitoring. The easy design and smaller storage capability of LF RFID tags make them extremely environment friendly for short-range purposes and cost-effective as effectively.
Really useful Merchandise

UHF On-Metallic LED Tag 60×20×3mm | ISO18000-6C
UHF LED RFID Grasp Tag 86×54×1mm | ISO18000-6C

RFID Silicone Wristband TK4100

RFID Silicone Wristband T5577


RFID Antenna UHF
15-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
UHF Tag
4″x2″ 860-960MHz UHF RFID Label RFID M4D
UHF Tag
4″x4″UHF RFID Label Alien H3 | ISO18000-6C
RFID Antenna UHF
5-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 1K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 4K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight C
HF Tag
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight EV1
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag ATA5577
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4200
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4305
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID TAG 213