
In modern security management, the importance of access control has become increasingly prominent, and ensuring the safety of personnel and resources has become the top priority for every organization. RFID technology offers a powerful solution to meet this need. Through contactless identification, RFID systems can efficiently and accurately manage access rights, significantly reducing security risks.
This technology is widely used in corporate offices, schools, medical institutions, and other places to help achieve real-time monitoring and convenient management. RFID not only effectively prevents unauthorized entry but also automatically records access behavior to enhance security and transparency. Combined with smart door locks and entry systems, RFID technology provides users with a fast and secure way to enter, making access management more efficient.
What is an RFID access control system?
An RFID access control system is a security management system based on radio frequency identification technology, designed to control and manage personnel access to specific areas. The system achieves contactless access control by identifying users carrying RFID tags and is widely used in enterprises, schools, hospitals, and other locations. Compared to traditional keys or passwords, RFID access control systems offer higher security and convenience, effectively preventing unauthorized entry and reducing management complexity.


Introduction to RFID and its classification
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a technology that identifies and tracks objects through radio waves. Its basic components include RFID tags, readers, and data management systems.
RFID tags can be classified into three categories: active, passive, and semi-active.
Active tags: These have built-in batteries and can actively send signals. They are typically used in applications that require long reading distances, such as logistics and asset tracking.
Passive tags: These do not have built-in batteries and rely on electromagnetic waves emitted by readers to activate. They are more common, cost-effective, and suitable for access control systems and ticket management.
Semi-active tags: While they have batteries, they still require external devices to activate. This type of tag is often used in battery-powered applications like temperature monitoring.

How does an RFID access control system work?
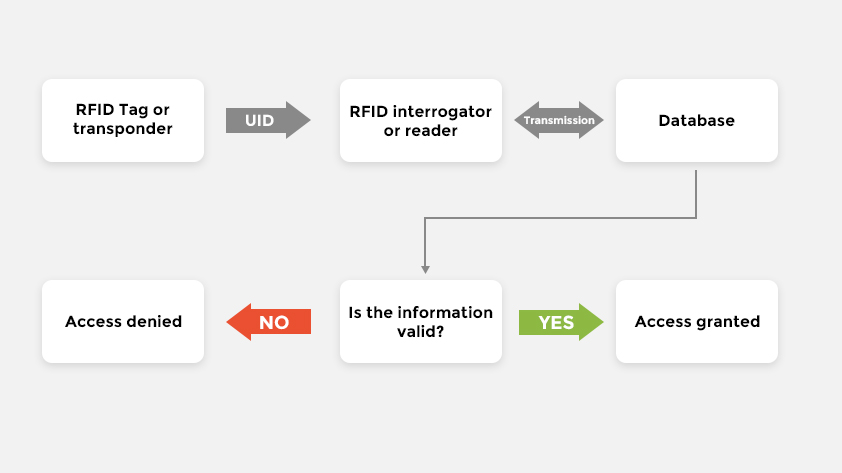
The working process of an RFID access control system is as follows:
Signal transmission: When a user brings an RFID tag close to the access control reader, the reader sends a radio frequency signal to activate the nearby RFID tag.
Information transmission: Upon receiving the signal, the RFID tag sends its unique identification information back to the reader via radio frequency signal.
Data verification: The reader transmits the received information to the central control system for verification. The central control system checks whether the identification information is on the authorized list.
Access control: If the information is authorized, the system sends a signal to unlock access; if not authorized, the system denies access and may trigger an alarm.
This process usually takes only a few seconds, ensuring a fast and secure access experience.

Classification of RFID access control systems
Based on operating frequency, RFID access control systems can be divided into three categories:
Low Frequency (LF) RFID
Low frequency RFID typically operates between 125kHz and 134kHz and is suitable for short-range identification (usually no more than 10 cm). Due to its strong anti-interference capability, LF RFID systems are often used in access control applications with high security requirements, such as garage access control and access card systems, ensuring that only authorized personnel can enter specific areas.
High Frequency (HF) RFID
HF RFID operates in the 13.56MHz frequency band, with identification distances ranging from several centimeters to 1 meter. This technology is widely used in access control systems, especially in campuses, enterprises, and public facilities. HF RFID systems not only support fast data transmission but also enable multi-user access simultaneously, improving the efficiency and security of access control management.
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID
UHF RFID operates in the 860MHz to 960MHz frequency band, with identification distances of up to ten meters or more. Its high reading speed and long-distance identification capabilities make it very suitable for access control management in large venues, such as warehouses, transportation centers, and large office buildings. UHF RFID systems can identify multiple tags in a single scan, providing efficient access control solutions for high-traffic areas, ensuring security while enhancing the user experience.


Composition of an RFID access control system
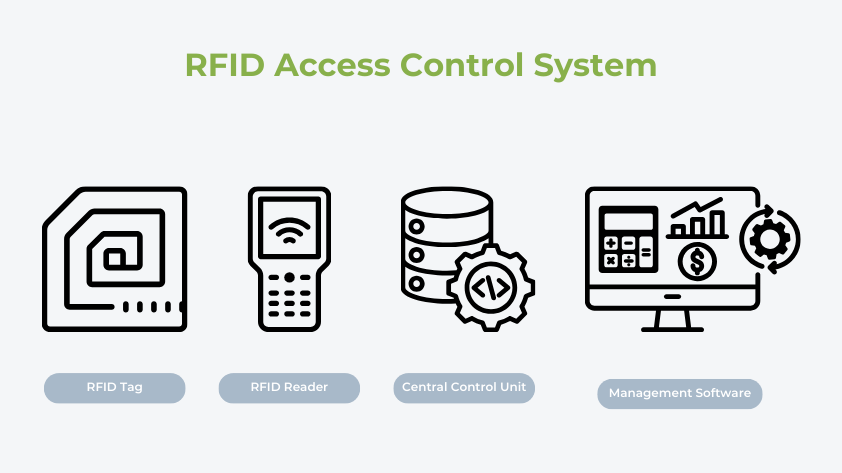
RFID access control systems mainly consist of the following key components:
RFID Tag: A device used to identify users, containing unique identity information. Users can wear cards, key fobs, or have them embedded in other items.
Reader: Responsible for sending radio frequency signals and receiving information sent back by RFID tags. It can be fixed (installed next to the door) or portable (handheld).
Central Control Unit: Used to process data from the reader, verify identity, and control access status. It is usually connected to a database to store user information and access rights.
Management Software: Provides user management, access rights settings, logging, and system monitoring functions. Administrators can view access control records and system status in real-time through the software, perform data analysis, and generate reports.
These components work together to achieve efficient and secure access control management, enhancing overall security and convenience.

Benefits of RFID access control system
Using an RFID access system not only enhances security but also improves management efficiency.
Enhancing security
Strengthening identity authentication
The RFID access control system provides multiple authentication methods to ensure that only authorized personnel can enter specific areas. Unlike traditional key systems, RFID tags can be linked to users’ personal information, eliminating the risk of keys being lost or copied.
Real-time monitoring and data recording
The RFID system can record information about individuals entering and exiting in real-time and generate detailed access logs. These logs not only assist with security audits but also provide data support for management. By analyzing access data, companies can identify potential security threats and take timely action.
Preventing safety hazards
The RFID access control system can set different access rights to restrict unnecessary entry. For example, sensitive areas may only be accessed by specific personnel, reducing internal safety risks. This hierarchical management approach is widely used in financial institutions and medical facilities to ensure the security of sensitive information and assets.
Improving management efficiency
Simplifying visitor management
The RFID access control system makes visitor management more efficient. Visitors only need to scan the RFID tag upon entry, and the system automatically records their information, eliminating the tedious manual registration process.
Reducing operating costs
By utilizing RFID technology, companies can lower the overall operating costs of security management. Traditional key management and personnel training require a significant investment of time and money, while the automation capabilities of the RFID system can greatly reduce the need for human resources. Additionally, the maintenance costs of RFID systems are usually lower than those of traditional systems.
Improving user experience
The RFID access control system provides a contactless entry method, allowing users to simply approach the reader to complete identity verification. This convenience significantly enhances the user experience, especially in high-traffic areas such as airports and large office buildings.


Integrating access control into a wider RFID security system
RFID technology not only enables efficient authentication and real-time monitoring but can also be deeply integrated with other security systems to further enhance overall security and management efficiency. This integration simplifies operational processes and strengthens the ability to respond to potential security threats. Below are some key application areas where RFID access control systems are integrated with other security systems, showcasing their important role in improving security management.
Video surveillance system
Combining RFID access control with a video surveillance system creates a comprehensive security solution. When the RFID system recognizes that a user enters or exits a specific area, the surveillance camera can automatically start recording and timestamp the footage. This integration provides real-time monitoring and allows for rapid playback of video footage after a security incident, aiding in investigations and evidence collection, ensuring that all activities are documented.
Intrusion alarm system
By integrating with an intrusion alarm system, an RFID access control system can immediately trigger an alarm when unauthorized entry is detected. For instance, when an RFID reader detects an unregistered tag attempting to access a sensitive area, the system automatically sends an alarm or notification to security personnel. This immediate response mechanism significantly enhances preventive capabilities, reduces potential security risks, and protects company assets and personnel.
Time and Attendance Management System
RFID technology can automatically record employee attendance information. By integrating with the time management system, companies can easily track employees’ clock-in and clock-out times. Whenever an employee swipes their card to enter or exit, the system automatically logs this information, reducing errors in manual entry. Moreover, this automated attendance record can generate reports, making it convenient for the human resources department to conduct payroll processing and attendance analysis, thus improving management efficiency.
Asset Management System
The application of RFID technology in asset management helps companies track and manage equipment and inventory in real-time. By combining RFID access control with the asset management system, companies can monitor which assets enter or leave a specific area within a given timeframe, ensuring the safety of critical equipment. This integration allows companies to reduce the risk of asset loss and theft, optimize inventory management, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Personnel Positioning System
In large venues such as airports, shopping malls, or industrial parks, RFID systems can be combined with personnel positioning technology to track personnel location information in real-time. This integration enables security personnel to quickly locate individuals in emergencies and ensures that all employees and visitors are in safe areas. Additionally, management can analyze personnel flow through data analysis to optimize space layout and security strategies.
Emergency Response System
In the event of a fire, natural disaster, or other emergencies, the RFID access control system can be integrated with the emergency response system to provide real-time data support. For example, when the RFID system identifies the number of people in a specific area, the emergency response team can quickly assess the situation on-site and ensure that all trapped individuals are rescued promptly. This data-driven approach not only enhances the efficiency of emergency responses but also minimizes losses and injuries.


Who can use RFID access control systems?
RFID access control systems have been widely adopted across various fields due to their flexibility and efficiency. Below are several major users and their specific applications:
Enterprises and companies
Businesses often utilize RFID access control systems to manage employee access and ensure the security of sensitive areas. By distributing RFID cards to employees, companies can monitor who enters the premises and when and where in real time. The system automatically records entry and exit times and generates access logs to assist HR departments in managing attendance. Additionally, RFID technology supports multiple permission settings, allowing different access rights for senior managers and regular employees, thereby enhancing overall security.
Educational institutions
Schools and universities play a crucial role in managing campus security. Students and faculty can use RFID cards to access dormitories, classrooms, and laboratories. This system not only simplifies visitor management but also tracks the flow of people on campus in real time, helping to detect safety hazards promptly. In emergencies, school administrators can quickly obtain a list of individuals on campus to ensure that everyone can be protected in a timely manner.
Medical institutions
Hospitals and clinics face strict security and privacy protection requirements. RFID access control systems effectively prevent unauthorized individuals from entering pharmacies, wards, and other sensitive areas. These systems not only safeguard patient privacy but also ensure that medical staff can quickly access medications and equipment as needed. Furthermore, RFID systems can be integrated with medical record management to ensure that only authorized medical personnel can access patient information, protecting patients’ personal data.
Government agencies
Government buildings and military bases have extremely high security requirements, making RFID access control systems indispensable. Through precise identity authentication and access management, these agencies can effectively control personnel entry and exit, preventing potential security threats. RFID systems also support real-time monitoring and alarm functions. If unauthorized entry attempts are detected, the system can immediately notify security personnel to ensure the safety of the country and the public.
Warehousing and logistics companies
In the warehousing and logistics sector, RFID technology can be employed to manage inventory and assets, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access specific areas. The system can track the entry and exit of goods in real time, reducing human errors and improving work efficiency. Additionally, RFID technology can be integrated with inventory management software to achieve real-time inventory monitoring, helping companies optimize their supply chain and reduce operating costs.
Commercial places
Shopping centers and entertainment facilities use RFID systems to enhance customer safety and convenience. Customers can enter venues contactlessly using RFID bracelets or cards, avoiding the hassle of traditional queuing and verification. Simultaneously, merchants can monitor customer flow in real time and provide data support for security management. RFID systems can also be employed for event management, such as sports events and concerts, to ensure audience safety and order.
Home users
High-end residential areas and smart homes have also started adopting RFID access control systems. Residents can easily enter and exit without contact using RFID tags, improving convenience. Additionally, the system can record the entry and exit of family members to enhance home security. Parents can also set up visitor management functions to restrict unauthorized entry, ensuring the safety of their families and property.
Stadiums and exhibition centers
In large-scale events and competitions, RFID access control systems can effectively manage spectator entry and exit. Spectators receive RFID wristbands when purchasing tickets and only need to scan them upon entry, reducing wait times in line. Moreover, the system can monitor crowd density in real time, assisting security personnel in adjusting security measures as needed to ensure the smooth running of the event.


Comparison of RFID Access Control Systems with Other Security Technologies
In the field of security management, various access control technologies each have their own advantages and disadvantages. Below is a comparison of RFID access control systems with several common security technologies:
RFID Access Control System vs. Password Access Control System
Security: RFID access control systems use a unique RFID tag (such as a card or bracelet) to authenticate the user. These tags typically have encryption features, making them difficult to copy or forge. In contrast, password access control systems are vulnerable to social engineering attacks, where someone might observe or obtain another person’s password and gain unauthorized access.
User Experience: The RFID system enables contactless identification. Users simply need to bring the tag close to the reader, greatly enhancing convenience and ease of use. Password access control requires users to enter a password, which can cause frustration if they input it incorrectly, especially during peak times.
Management: The RFID system can automatically generate entry and exit records, making it easy for later audits and data analysis. On the other hand, password systems usually require manual logging, lack real-time monitoring capabilities, and are less efficient for management.
RFID Access Control System vs. Biometrics
Accuracy: Biometrics (like fingerprint, facial, or iris recognition) provide high accuracy in identity verification and are nearly impossible to forge or misuse. However, these systems can have risks of misidentification, particularly in low light or if fingerprints are damaged.
Cost: RFID systems are relatively economical, with low equipment and maintenance costs, making them suitable for large-scale deployment. Biometric systems typically require a higher initial investment, with increased complexity in equipment and software, as well as higher maintenance and upgrade costs.
User Acceptance: Most people have a positive attitude toward using RFID cards or tags because they are easy to operate. Biometrics, however, may raise privacy concerns, and some users might be hesitant to use them for that reason.
RFID Access Control System vs. Magnetic Card System
Security: RFID tags provide higher security because they are designed to be difficult to copy. In contrast, counterfeiters can easily replicate magnetic cards, especially under certain technical conditions, and users can easily damage their magnetic stripes during use.
Durability: RFID tags are generally waterproof and dustproof, making them suitable for various environments. In contrast, magnetic cards can wear out quickly with daily use and perform poorly in adverse weather conditions, often requiring frequent replacements.
Reading Distance: RFID systems can achieve contactless identification, usually within a range of several centimeters to over ten meters, while magnetic cards require physical contact with the card reader, which is cumbersome and reduces access efficiency.
RFID Access Control System vs. Traditional Keys
Security: Traditional keys are easy to copy, lose, or steal, and picking a lock significantly lowers security. RFID systems quickly update permissions electronically when someone loses a card, reducing risks.
Convenience: RFID systems support fast passage. Users only need to present or bring the RFID card close to the reader to gain access, while traditional keys require insertion into locks, which consumes time and effort, especially at gates or high-traffic areas.
Flexibility: RFID systems enable you to change user permissions at any time. For example, you can immediately revoke access rights when an employee leaves. In contrast, if you lose a traditional key, you usually need to replace the entire set of locks, which is time-consuming and costly.
RFID Access Control System vs. Internet of Things (IoT) Security System
Technology Integration: RFID access control systems can be part of the IoT ecosystem, integrated with smart cameras, sensors, and alarm systems to achieve real-time monitoring and more efficient management. IoT technology enhances data analysis capabilities and can monitor security conditions in real time.
Real-Time Data: IoT systems can provide real-time data feedback and analysis to support data-driven decision-making. RFID systems, however, mainly focus on identity recognition and access control, and have relatively weak data analysis capabilities, requiring integration with other systems to achieve this.
Cost and Complexity: IoT systems tend to have high design and maintenance costs, making them suitable for companies with high demands for data analysis and comprehensive monitoring. RFID systems provide a relatively simple and economical solution that meets basic access control needs.
It can be seen that, RFID access control systems have clear advantages in terms of convenience, security, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for a variety of environments. However, choosing the right access control technology still requires a comprehensive evaluation based on the organization’s specific needs, budget, and security goals. Each technology has its applicable scenarios, and a combined use of different technologies can achieve the best security outcomes.


Considerations for using RFID access control systems
When implementing RFID access control systems, there are several important considerations to keep in mind:
Choosing the right type of tag
It is crucial to select the appropriate RFID tag based on specific application requirements. Active tags have built-in batteries and are suitable for scenarios requiring a longer reading distance, such as large warehouses; passive tags do not have batteries and are ideal for everyday access control management due to their low cost and ease of maintenance. Semi-active tags combine characteristics of both and are suitable for applications needing regular information updates. Choosing the right type of tag based on environmental factors (like temperature and humidity) and the frequency of tag use can ensure the system’s stability and reliability.
System security
The security of the RFID system directly impacts the overall effectiveness of security management. Strong encryption algorithms (such as AES or RSA) should be employed to protect data security during transmission. Setting complex access passwords and changing them regularly can effectively prevent unauthorized personnel from accessing the system. Additionally, you can establish multiple authentication mechanisms, such as integrating biometrics, to further enhance security and reduce the risk of hacking.
Reader location
The positioning of RFID readers is critical to system performance. The placement of readers should be strategically planned according to site conditions and user traffic to ensure coverage of all key areas. Avoid obstacles (like metal objects and walls) that can interfere with the signal to maintain signal strength and reading accuracy. At high-traffic entry and exit points, ensure that the reader’s reading speed is fast enough to minimize wait times.
Regular maintenance and updates
The software for RFID devices and systems requires regular maintenance and updates to maintain optimal performance. Regularly check hardware connections and device status, and promptly replace damaged parts. Additionally, pay attention to updates and patches released by manufacturers to ensure that the system addresses known vulnerabilities and errors. Maintenance records should be reviewed regularly to ensure compliance with established security standards and procedures.
User training
Providing systematic training for all employees using RFID access control systems is essential. Training content should include basic system operations, solutions to common problems, and safe usage guidelines. Ensure that employees understand how to use RFID cards correctly and avoid sharing them with others to prevent potential security risks. Regular training sessions and drills should be held to enhance employees’ security awareness.
Data privacy protection
When implementing RFID access control systems, relevant data protection regulations (such as GDPR) should be adhered to. Ensure that the storage and processing of user data meet privacy protection requirements. Regularly review data access rights to limit access to sensitive information to only necessary personnel. Establish transparency in data processing and storage so that users understand the purpose and handling of their data, thereby enhancing trust.
Backup and recovery plan
Establish a comprehensive data backup and recovery plan to prevent losses from system failures or data loss. Perform regular data backups and ensure that backup data is securely stored offsite. Develop a clear recovery process that includes contact information and recovery steps for key personnel, enabling a quick response in the event of a failure to ensure business continuity.
Integration with other systems
When integrating the RFID access control system with other security systems (such as monitoring, alarm, or personnel management systems), ensure data compatibility between the systems. Establish an effective data sharing mechanism to facilitate real-time monitoring and response. Regularly test the integration to ensure smooth collaboration between different systems and improve overall security management efficiency.


Conclusion
In conclusion, RFID access control systems play a vital role in modern security management by offering efficient, flexible, and reliable solutions for a variety of settings. By enabling contactless identity authentication and real-time permission management, RFID technology significantly enhances security and user experience, making it suitable for environments such as businesses, educational institutions, and healthcare facilities.
When selecting and implementing RFID access control systems, users need to carefully consider their specific requirements, budgets, and how well the system can integrate with existing infrastructures. Effective planning and well-thought-out implementation strategies will help maximize the benefits of the system. Additionally, it’s important to be mindful of relevant usage guidelines and maintenance practices to ensure the system remains in optimal operating condition.
As technology continues to advance, we expect RFID access control systems to become even more intelligent, potentially integrating with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and big data analytics to enhance security management capabilities. In the face of increasingly complex security challenges, choosing the right access control system will provide stronger protection for businesses and institutions.
FAQs
1. What are the advantages of RFID access control systems?
RFID access control systems offer multiple advantages, including efficiency and convenience. Compared to traditional key or password systems, RFID systems enable fast contactless identification, allowing users to simply bring the RFID card close to the reader. The system can also generate real-time entry and exit records for easy management and auditing. Additionally, RFID technology supports multiple user rights management, enabling companies to flexibly adjust access rights based on employee positions and needs to enhance security.
2. What are the components of RFID access control systems?
A complete RFID access control system typically consists of three main components: RFID tags, readers and writers, and management software. Users attach RFID tags as identification devices, while readers and writers send and receive signals to read tag information. Management software processes data and manages permissions. These components work together to achieve effective control and monitoring of personnel entry and exit.
3. What industries are RFID access control systems suitable for?
RFID access control systems are suitable for various industries, including enterprises, education, medical institutions, and government agencies. Businesses use RFID systems to control the entry and exit of employees and visitors, thereby improving workplace safety. Educational institutions can manage campus security to ensure the safety of students and faculty. Medical institutions can utilize RFID systems to protect pharmacies and sensitive areas from unauthorized access. Additionally, government agencies and military bases employ RFID technology to manage confidential information and protect critical facilities.
4. Does the RFID access control system require maintenance?
Yes, RFID access control systems require regular maintenance to ensure proper functionality. This includes routine inspections and updates of hardware (such as readers and tags), software upgrades, and system security assessments. The maintenance process also involves reviewing access logs to identify potential security vulnerabilities. Moreover, training users to ensure familiarity with system operations is part of the maintenance process.
5. How long does it take to implement an RFID access control system?
The time required to implement an RFID access control system varies based on the size and complexity of the project. Typically, simple systems can be installed and put into operation within a few days, while larger systems may take weeks to months. This process includes multiple stages such as demand analysis, equipment procurement, system configuration, installation and commissioning, and user training. During implementation, ensure effective communication with the supplier to resolve any technical issues promptly.
Rec-Products

ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4200

RFID Silicone Wristband MIFARE Ultralight® C
This MIFARE Ultralight® C RFID silicone wristband offers outstanding performance and security features. It is designed for contactless smart ticket applications. With advanced 3DES authentication and unique serial number technology, it effectively prevents data cloning or tampering, ensuring strong security for user information. Tailored for use in public transport, event tickets, hospitality and loyalty programs, it’s the perfect choice for those seeking both convenience and security.

NXP MIFARE Classic®EV1 1k (S50) RFID Card ISO14443-A CR80
![]()
The NXP Mifare® Classic 1k EV1 (Mifare® S50) blank RFID Cards are fully comply with ISO14443-A. The RFID cards are made with Photo-quality standard PVC/PET in the size of CR80, which are suitable for use with most thermal transfer card printers.

RFID Antenna UHF
15-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
UHF Tag
4″x2″ 860-960MHz UHF RFID Label RFID M4D
UHF Tag
4″x4″UHF RFID Label Alien H3 | ISO18000-6C
RFID Antenna UHF
5-Meter Cable for UHF RFID Fixed Reader
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 1K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Classic 4K
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight C
HF Tag
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID Ultralight EV1
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag ATA5577
LF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4200
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag EM4305
HF Card
ABS RFID KEY-FOB Tag RFID TAG 213